A review of therapeutic potentials of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L.) and its main constituent, silymarin, on cancer, and their related patents
- PMID: 36311193
- PMCID: PMC9588316
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.63200.13961
A review of therapeutic potentials of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L.) and its main constituent, silymarin, on cancer, and their related patents
Abstract
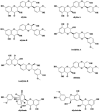
For more than 2000 years, Silybum marianum L. (milk thistle) has been used for treating different complications such as jaundice, hepatitis, and cancers. It has also been shown that silymarin, a flavonolignan extract of the plant, demonstrates chemopreventive effects against cancers. This patent review presents and discusses recent patents concerning the anticancer effects of S. marianum and silymarin. The data were gathered by searching an extensive literature review conducted in Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Google Patent, Patent Scope, and US Patent. Milk thistle and silymarin have been used in a variety of medical, therapeutic, and pharmaceutical fields, according to a large number of documents and patents. Milk thistle and silymarin have been used as complementary treatments for cancers such as skin, prostate, and colorectal cancers, as well as hepatoprotective agents. Silymarin exerts a chemopreventive effect on reactivating cell death pathways by modulation of the antiapoptotic proteins and synergizing with agonists of death domain receptors. Based on the results of these patents, silymarin could be beneficial to oncology patients, especially for the treatment of the side effects of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Following the human propensity to use phytocompounds rather than medicines based on chemical constituents, special attention must be paid to tie the value of milk thistle and silymarin from basic science to clinical applications.
Keywords: Anti-oxidants; Antineoplastic agents; Milk thistle; Neoplasms; Pharmaceutical – preparations; Plant extracts; Silybum marianum L. Silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Milk Thistle (Silybum Marianum) as a Supportive Phytotherapeutic Agent in Oncology].Klin Onkol. 2017 Winter;30(6):426-432. doi: 10.14735/amko2017426. Klin Onkol. 2017. PMID: 29271213 Review. Czech.
-
Silymarin (milk thistle extract) as a therapeutic agent in gastrointestinal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;142:112024. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112024. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34399200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silybum marianum (milk thistle) and its main constituent, silymarin, as a potential therapeutic plant in metabolic syndrome: A review.Phytother Res. 2018 Oct;32(10):1933-1949. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6153. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30015401 Review.
-
Determination of Flavonolignan Compositional Ratios in Silybum marianum (Milk Thistle) Extracts Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography.Molecules. 2024 Jun 21;29(13):2949. doi: 10.3390/molecules29132949. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38998902 Free PMC article.
-
New therapeutic potentials of milk thistle (Silybum marianum).Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Dec;8(12):1801-10. Nat Prod Commun. 2013. PMID: 24555302 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Viral Activity of Bioactive Molecules of Silymarin against COVID-19 via In Silico Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 17;16(10):1479. doi: 10.3390/ph16101479. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895950 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Silymarin, Spirulina platensis, and Chlorella vulgaris towards Cardiotoxicity via Modulating Antioxidant Activity, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(10):1289. doi: 10.3390/life14101289. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459589 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine approach to relieving dyspnea: A narrative review of efficacy and mechanisms.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(9):1140-1162. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.85518.18486. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40809176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Herbal Interventions for the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024;20(5):e030524229664. doi: 10.2174/011573403X286573240422104647. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38706368 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights into Silymarin-Induced Apoptosis and Growth Inhibition in SPC212 Human Mesothelioma Cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):2405-2414. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01650-w. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39747779
References
-
- Angeli JP, Barcelos GR, Serpeloni JM, Barbosa F Jr, Nersesyan A, Mantovani MS. Evaluation of the genotoxic and anti-genotoxic activities of silybin in human hepatoma cells (HepG2) Mutagenesis. 2010;25:223–229. - PubMed
-
- Ansari D, Tingstedt B, Andersson B, Holmquist F, Sturesson C, Williamsson C, et al. Pancreatic cancer: yesterday, today and tomorrow. Future Oncol. 2016;12:1929–1946. - PubMed
-
- Barros TMB, Lima APB, Almeida TC, da Silva GN. Inhibition of urinary bladder cancer cell proliferation by silibinin. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020;61:445–455. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous