CXCR6 expressing T cells: Functions and role in the control of tumors
- PMID: 36311728
- PMCID: PMC9597613
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1022136
CXCR6 expressing T cells: Functions and role in the control of tumors
Abstract
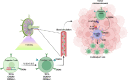
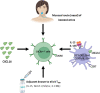
CXCR6 is a receptor for the chemokine CXCL16, which exists as a membrane or soluble form. CXCR6 is a marker for resident memory T (TRM) cells that plays a role in immunosurveillance through their interaction with epithelial cells. The interaction of CXCR6 with CXCL16 expressed at the membrane of certain subpopulations of intratumor dendritic cells (DC) called DC3, ideally positions these CXCR6+ T cells to receive a proliferation signal from IL-15 also presented by DC3. Mice deficient in cxcr6 or blocking the interaction of CXCR6 with its ligand, experience a poorer control of tumor proliferation by CD8+ T cells, but also by NKT cells especially in the liver. Intranasal vaccination induces CXCL16 production in the lungs and is associated with infiltration by TRM expressing CXCR6, which are then required for the efficacy of anti-tumor vaccination. Therapeutically, the addition of CXCR6 to specific CAR-T cells enhances their intratumoral accumulation and prolongs survival in animal models of pancreatic, ovarian and lung cancer. Finally, CXCR6 is part of immunological signatures that predict response to immunotherapy based on anti-PD-(L)1 in various cancers. In contrast, a protumoral role of CXCR6+T cells has also been reported mainly in Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) due to a non-antigen specific mechanism. The targeting and amplification of antigen-specific TRM expressing CXCR6 and its potential use as a biomarker of response to immunotherapy opens new perspectives in cancer treatment.
Keywords: CAR T cell; CXCL16; CXCR6; dendritic cell; immunotherapy; mucosal vaccination; resident memory T cell.
Copyright © 2022 Mabrouk, Tran, Sam, Pourmir, Gruel, Granier, Pineau, Gey, Kobold, Fabre and Tartour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

