Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with cardiovascular outcome and safety events: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
- PMID: 36312269
- PMCID: PMC9613919
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.926979
Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with cardiovascular outcome and safety events: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Abstract
Background: The clinical benefit of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for preventing and treating cardiovascular events remains controversial. We aimed to study the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes and safety events, giving particular attention to the benefits in subgroups of patients with different diseases.
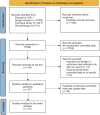
Method: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reporting cardiovascular outcomes following the administration of SGLT2 inhibitors and placebo were included in this study. Cardiovascular outcomes included all-cause death, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), cardiovascular (CV) death, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and hospitalization for heart failure (HHF). We also focused on the cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2 inhibitor application in subgroups of patients with different diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), heart failure (HF), high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ACD), diagnosed ACD, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Safety events associated with SGLT2 inhibitors, including acute kidney injury (AKI), diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hypoglycemia, urinary tract infection, thromboembolic event, bone fracture, volume depletion, and amputation, were also reported.
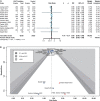
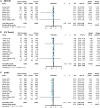
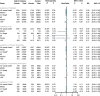
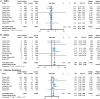
Results: This meta-analysis included 15 RCTs with 78,212 participants. SGLT2 inhibitors reduced the risk of all-cause death (RR 0.89; 95% CI: 0.85-0.94; I2 = 32%; p < 0.01), CV death (RR 0.87; 95% CI: 0.82-0.93; I2 = 11%; p < 0.01), MACEs (RR 0.89; 95% CI: 0.84-0.94; I2 = 46%; p < 0.01), HHF (RR 0.70; 95% CI: 0.66-0.74; I2 = 0%; p < 0.01), and AKI (RR 0.81; 95% CI: 0.73-0.90; I2 = 0%; p < 0.01) but increased the risk of DKA (RR 2.56; 95% CI: 1.72-3.80; I2 = 0%; p < 0.01). However, no apparent benefit in MI and stroke was observed between the SGLT2 inhibitor and control groups. SGLT2 inhibitors reduced the risk of all-cause death, MACEs, CV death, and HHF in diabetic patients; reduced the risk of all-cause death, MACEs, CV death, MI, and HHF in primary prevention; reduced the risk of all-cause death, CV death, and HHF in patients with ACD and HF; and reduced the risk of MACEs, CV death, and HHF in patients with CKD.
Conclusion: SGLT2 inhibitors have a positive effect in reducing the risk of all-cause death, CV death, MACE, HHF, and AKI and increasing the risk of DKA. The application of SGLT2 inhibitors in the primary prevention of ACD also has certain clinical benefits in reducing MI.
Systematic review registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42022306490].
Keywords: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular risks; diabetes; heart failure; sodium-glucose cotransoporter-2 inhibitors.
Copyright © 2022 Gong, Shen, Zhang, Zhou, Shen, Zhao, Ding, Ma and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors With Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Feb 1;6(2):148-158. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4511. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33031522 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients with Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 23;61(2):202. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020202. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005319 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in myocardial infarction patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Mar;27(3):1276-1286. doi: 10.1111/dom.16122. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39691984
-
Differential effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on cardiovascular and renal outcomes according to renal function: a dose-response meta-analysis involving 10 randomized clinical trials and 71 553 individuals.Eur J Endocrinol. 2023 Jul 20;189(1):S17-S25. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad078. Eur J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37474112
-
Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 4;9:875327. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.875327. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35600478 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hypoglycemic agents and bone health; an umbrella systematic review of the clinical trials' meta-analysis studies.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Dec 23;16(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01518-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39716250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibition on systemic hemodynamics, renal function, and intra-renal oxygenation in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024 Jul 8;12(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40635-024-00647-2. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024. PMID: 38977627 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors and Their Impact on the Management of Heart Failure.Cureus. 2024 Dec 16;16(12):e75802. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75802. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39816302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors from a glucose-lowering drug to a pivotal therapeutic agent for cardio-renal-metabolic syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 30;14:1111984. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1111984. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36793276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Renoprotective Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i)-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7057. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137057. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wright EM, Loo DD, Hirayama BA. Biology of human sodium glucose transporters. Physiol Rev. (2011) 91:733–94. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

