A Scoping Review and Appraisal of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Education Literature
- PMID: 36312813
- PMCID: PMC9585707
- DOI: 10.34197/ats-scholar.2022-0058RE
A Scoping Review and Appraisal of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Education Literature
Abstract
Background: Despite a recent rise in publications describing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) education, the scope and quality of ECMO educational research and curricular assessments have not previously been evaluated.
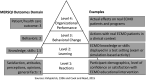
Objective: The purposes of this study are 1) to categorize published ECMO educational scholarship according to Bloom's educational domains, learner groups, and content delivery methods; 2) to assess ECMO educational scholarship quality; and 3) to identify areas of focus for future curricular development and educational research.
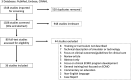
Methods: A multidisciplinary research team conducted a scoping review of ECMO literature published between January 2009 and October 2021 using established frameworks. The Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument (MERSQI) was applied to assess quality.
Results: A total of 1,028 references were retrieved; 36 were selected for review. ECMO education studies frequently targeted the cognitive domain (78%), with 17% of studies targeting the psychomotor domain alone and 33% of studies targeting combinations of the cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains. Thirty-three studies qualified for MERSQI scoring, with a median score of 11 (interquartile range, 4; possible range, 5-18). Simulation-based training was used in 97%, with 50% of studies targeting physicians and one other discipline.
Conclusion: ECMO education frequently incorporates simulation and spans all domains of Bloom's taxonomy. Overall, MERSQI scores for ECMO education studies are similar to those for other simulation-based medical education studies. However, developing assessment tools with multisource validity evidence and conducting multienvironment studies would strengthen future work. The creation of a collaborative ECMO educational network would increase standardization and reproducibility in ECMO training, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument; curricula; education; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; scoping review.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Thoracic Society.
Figures
References
-
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Ann Arbor, MI: Extracorporeal Life Support Organization; 2022. https://www.elso.org/Portals/0/Files/Reports/2022_April/Trend%20Report%2...
-
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Ann Arbor, MI: Extracorporeal Life Support Organization; 2010. https://www.elso.org/Portals/0/IGD/Archive/FileManager/97000963d6cuserss...
-
- Muratore S, Beilman G, John R, Brunsvold M. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation credentialing: where do we stand? Am J Surg . 2015;210:655–660.e2. - PubMed
-
- Abulebda K, Hocutt GRNC, Gray BW, Ahmed RA, Slaven JE, Malin S, et al. Development of validated checklists to evaluate clinical specialists in pediatric ECMO emergencies using Delphi method. ASAIO J . 2020;66:314–318. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

