ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and its Implications in Aging Pathways
- PMID: 36312897
- PMCID: PMC9605829
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1225578
ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and its Implications in Aging Pathways
Abstract
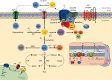
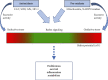
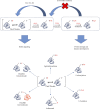
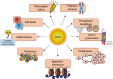
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are bioproducts of cellular metabolism. There is a range of molecules with oxidizing properties known as ROS. Despite those molecules being implied negatively in aging and numerous diseases, their key role in cellular signaling is evident. ROS control several biological processes such as inflammation, proliferation, and cell death. The redox signaling underlying these cellular events is one characteristic of the new generation of scientists aimed at defining the role of ROS in the cellular environment. The control of redox potential, which includes the balance of the sources of ROS and the antioxidant system, implies an important target for understanding the cells' fate derived from redox signaling. In this review, we summarized the chemical, the redox balance, the signaling, and the implications of ROS in biological aging.
Copyright © 2022 Arthur José Pontes Oliveira de Almeida et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

