Interplay between the microalgae Micrasterias radians and its symbiont Dyadobacter sp. HH091
- PMID: 36312980
- PMCID: PMC9606717
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1006609
Interplay between the microalgae Micrasterias radians and its symbiont Dyadobacter sp. HH091
Abstract
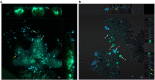
Based on previous research, related to detailed insight into mutualistic collaboration of microalga and its microbiome, we established an artificial plant-bacteria system of the microalga Micrasterias radians MZCH 672 and the bacterial isolate Dyadobacter sp. HH091. The bacteria, affiliated with the phylum Bacteroidota, strongly stimulated growth of the microalga when it was added to axenic algal cultures. For further advances, we studied the isolate HH091 and its interaction with the microalga M. radians using transcriptome and extensive genome analyses. The genome of HH091 contains predicted polysaccharide utilizing gene clusters co-working with the type IX secretion system (T9SS) and conceivably involved in the algae-bacteria liaison. Here, we focus on characterizing the mechanism of T9SS, implementing the attachment and invasion of microalga by Dyadobacter sp. HH091. Omics analysis exposed T9SS genes: gldK, gldL, gldM, gldN, sprA, sprE, sprF, sprT, porU and porV. Besides, gld genes not considered as the T9SS components but required for gliding motility and protein secretion (gldA, gldB, gldD, gldF, gldG, gldH, gldI, gldJ), were also identified at this analysis. A first model of T9SS apparatus of Dyadobacter was proposed in a course of this research. Using the combination of fluorescence labeling of Dyadobacter sp. HH091, we examined the bacterial colonisation and penetration into the cell wall of the algal host M. radians MZCH 672.
Keywords: Dyadobacter sp. HH091; Micrasterias radians; microalgaebacteria interaction; symbiotic relations; synthetic early plant-bacteria system.
Copyright © 2022 Astafyeva, Gurschke, Streit and Krohn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
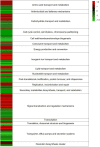
 up-regulated genes,
up-regulated genes,  down-regulated genes.
down-regulated genes.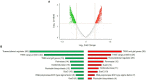
 up-regulated genes,
up-regulated genes,  down-regulated genes.
down-regulated genes.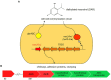
 up-regulated genes,
up-regulated genes,  down-regulated genes. (B) Expression levels of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) involved into flexirubin biosynthesis: dar and flx clusters, and transport systems (ATP binding cassettes (ABC)-transporters and hypothetical proteins).
down-regulated genes. (B) Expression levels of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) involved into flexirubin biosynthesis: dar and flx clusters, and transport systems (ATP binding cassettes (ABC)-transporters and hypothetical proteins).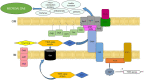
Similar articles
-
Untangling Flavobacterium johnsoniae Gliding Motility and Protein Secretion.J Bacteriol. 2017 Dec 20;200(2):e00362-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00362-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 29109184 Free PMC article.
-
Flavobacterium johnsoniae GldK, GldL, GldM, and SprA are required for secretion of the cell surface gliding motility adhesins SprB and RemA.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jul;195(14):3201-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00333-13. Epub 2013 May 10. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23667240 Free PMC article.
-
Flavobacterium johnsoniae PorV is required for secretion of a subset of proteins targeted to the type IX secretion system.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan 1;197(1):147-58. doi: 10.1128/JB.02085-14. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25331433 Free PMC article.
-
Type IX secretion: the generation of bacterial cell surface coatings involved in virulence, gliding motility and the degradation of complex biopolymers.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Oct;106(1):35-53. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13752. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28714554 Review.
-
The Type IX Secretion System: Advances in Structure, Function and Organisation.Microorganisms. 2020 Aug 1;8(8):1173. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081173. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32752268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A journey with type IX secretion system effectors: selection, transport, processing and activities.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Apr;169(4):001320. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001320. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 37043368 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Abscisic Acid on Growth, Fatty Acid Profile, and Pigment Composition of the Chlorophyte Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis and Its Co-Culture Microbiome.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 6;13(2):452. doi: 10.3390/life13020452. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836809 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into the C-terminal signal domain of the Bacteroidetes type-IX secretion system.Open Biol. 2024 Jun;14(6):230448. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230448. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38862016 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological, beneficial, and pathogenic functions of the Type 9 Secretion System.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Jun;17(6):e14516. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14516. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38924452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of the Antimicrobial Potential of the Arthrospira platensis, Planktothrix agardhii, Leptolyngbya cf. ectocarpi, Roholtiella mixta nov., Tetraselmis viridis, and Nanofrustulum shiloi against Gram-Positive, Gram-Negative Bacteria, and Mycobacteria.Mar Drugs. 2023 Sep 14;21(9):492. doi: 10.3390/md21090492. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37755105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen R. A. (2005). Algal Culturing Techniques. College Park, MD: Phycological Society of America.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

