Development, validation and clinical utility of a risk prediction model for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes: The PeRSonal GDM model
- PMID: 36313142
- PMCID: PMC9596305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101637
Development, validation and clinical utility of a risk prediction model for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes: The PeRSonal GDM model
Abstract
Background: The ability to calculate the absolute risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes for an individual woman with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) would allow preventative and therapeutic interventions to be delivered to women at high-risk, sparing women at low-risk from unnecessary care. We aimed to develop, validate and evaluate the clinical utility of a prediction model for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with GDM.
Methods: A prediction model development and validation study was conducted on data from a observational cohort. Participants included all women with GDM from three metropolitan tertiary teaching hospitals in Melbourne, Australia. The development cohort comprised those who delivered between 1 July 2017 to 30 June 2018 and the validation cohort those who delivered between 1 July 2018 to 31 December 2018. The main outcome was a composite of critically important maternal and perinatal complications (hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, large-for-gestational age neonate, neonatal hypoglycaemia requiring intravenous therapy, shoulder dystocia, perinatal death, neonatal bone fracture and nerve palsy). Model performance was measured in terms of discrimination and calibration and clinical utility evaluated using decision curve analysis.
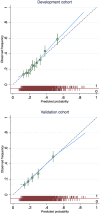
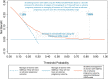
Findings: The final PeRSonal (Prediction for Risk Stratified care for women with GDM) model included body mass index, maternal age, fasting and 1-hour glucose values (75-g oral glucose tolerance test), gestational age at GDM diagnosis, Southern and Central Asian ethnicity, East Asian ethnicity, nulliparity, past delivery of an large-for-gestational age neonate, past pre-eclampsia, GWG until GDM diagnosis, and family history of diabetes. The composite adverse pregnancy outcome occurred in 27% (476/1747) of women in the development (1747 women) and in 26% (244/955) in the validation (955 women) cohorts. The model showed excellent calibration with slope of 0.99 (95% CI 0.75 to 1.23) and acceptable discrimination (c-statistic 0.68; 95% CI 0.64 to 0.72) when temporally validated. Decision curve analysis demonstrated that the model was useful across a range of predicted probability thresholds between 0.15 and 0.85 for adverse pregnancy outcomes compared to the alternatives of managing all women with GDM as if they will or will not have an adverse pregnancy outcome.
Interpretation: The PeRSonal GDM model comprising of routinely available clinical data shows compelling performance, is transportable across time, and has clinical utility across a range of predicted probabilities. Further external validation of the model to a more disparate population is now needed to assess the generalisability to different centres, community based care and low resource settings, other healthcare systems and to different GDM diagnostic criteria.
Funding: This work is supported by the Mothers and Gestational Diabetes in Australia 2 NHMRC funded project #1170847.
Keywords: Adverse pregnancy outcomes; Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM); Large-for-gestational age (LGA); Neonatal hypoglycaemia; Pre-eclampsia; Prediction model; Pregnancy complications; Prognosis; Risk-stratification.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SDC reports grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), Diabetes Australia, the Australian Academy of Science and the Australian Government Department of Education and Training during the conduct of the study; JAB reports grants from the NHMRC during the conduct of the study; BMFF reports grants from CIBER (Biomedical Research Network in Epidemiology and Public Health, Madrid, Spain) during the conduct of the study and HJT reports grants from the NHMRC and the Medical Research Future Fund during the conduct of the study; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. All the other authors report no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance National Diabetes Data Group. Diabetes. 1979;28(12):1039–1057. - PubMed
-
- McIntyre HD, Catalano P, Zhang C, Desoye G, Mathiesen ER, Damm P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):47. - PubMed
-
- Scifres C, Feghali M, Althouse AD, Caritis S, Catov J. Adverse outcomes and potential targets for intervention in gestational diabetes and obesity. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(2):316–325. - PubMed
-
- Huet J, Beucher G, Rod A, Morello R, Dreyfus M. Joint impact of gestational diabetes and obesity on perinatal outcomes. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2018;47(9):469–476. - PubMed
-
- Yuen L, Wong VW, Simmons D. Ethnic disparities in gestational diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(9):68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

