Increased Aurora B expression reduces substrate phosphorylation and induces chromosomal instability
- PMID: 36313574
- PMCID: PMC9606593
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1018161
Increased Aurora B expression reduces substrate phosphorylation and induces chromosomal instability
Abstract
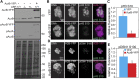
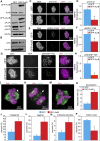
Increased Aurora B protein expression, which is common in cancers, is expected to increase Aurora B kinase activity, yielding elevated phosphorylation of Aurora B substrates. In contrast, here we show that elevated expression of Aurora B reduces phosphorylation of six different Aurora B substrates across three species and causes defects consistent with Aurora B inhibition. Complexes of Aurora B and its binding partner INCENP autophosphorylate in trans to achieve full Aurora B activation. Increased expression of Aurora B mislocalizes INCENP, reducing the local concentration of Aurora B:INCENP complexes at the inner centromere/kinetochore. Co-expression of INCENP rescues Aurora B kinase activity and mitotic defects caused by elevated Aurora B. However, INCENP expression is not elevated in concert with Aurora B in breast cancer, and increased expression of Aurora B causes resistance rather than hypersensitivity to Aurora B inhibitors. Thus, increased Aurora B expression reduces, rather than increases, Aurora B kinase activity.
Keywords: CIN; aurora kinase inhibitor; mitosis; mitotic checkpoint; spindle assembly checkpoint.
Copyright © 2022 Britigan, Wan, Sam, Copeland, Lasek, Hrycyniak, Wang, Audhya, Burkard, Roopra and Weaver.
Conflict of interest statement
M.E.B is a member of the Medical advisory board of Strata Oncology and receives Research funding from Abbvie, Genentech, Puma, Arcus, Apollomics, Loxo Oncology/Lilly, Seagen and Elevation Oncology. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Adams R. R., Wheatleya S. P., Gouldsworthy A. M., Kandels-Lewis S. E., Carmena M., Smythe C., et al. (2000). INCENP binds the Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to chromosomes, the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr. Biol. 10 (17), 1075–1078. 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00673-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adams R. R., Maiato H., Earnshaw W. C., Carmena M. (2001). Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J. Cell. Biol. 153 (4), 865–880. 10.1083/jcb.153.4.865 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azzariti A., Bocci G., Porcelli L., Fioravanti A., Sini P., Simone G. M., et al. (2011). Aurora B kinase inhibitor AZD1152: Determinants of action and ability to enhance chemotherapeutics effectiveness in pancreatic and colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 104 (5), 769–780. 10.1038/bjc.2011.21 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

