High genotypic diversity of human papillomavirus among women in Cameroon: implications for vaccine effectiveness
- PMID: 36313603
- PMCID: PMC9596729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.09.014
High genotypic diversity of human papillomavirus among women in Cameroon: implications for vaccine effectiveness
Abstract
Background: The burden of human papillomavirus (HPV) is high in Cameroon, but knowledge on high-risk oncogenic HPV (HR-HPV) is limited. Our study sought to ascertain the HR-HPV genotypes circulating in Cameroon.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among non-vaccinated women in Cameroon. Detection of HR-HPV was performed by real-time PCR on cervico-vaginal swabs. Predictors of HR-HPV were determined following logistic regression analysis, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
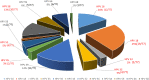
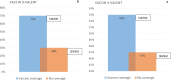
Results: In total, 364 women were enrolled, with a median age of 41 (34-50) years. Of these, 3.0% were smokers and 26.09% reported having more than three sexual partners. The overall HR-HPV positivity rate was 21.43% (95% CI 17.21-25.64). Predictors of HR-HPV were young age, i.e < 41 years (aOR (95% CI) 0.408 (0.194-0.862); p = 0.018), smoking (aOR 5.199 (1.314-20.575); p = 0.018), and having more than three sex partners (aOR: 2.335 (1.133-4.811); p = 0.022). Overall, 12 HR-HPV genotypes were identified, with 26.98% women coinfected with at least two HR-HPVs, including one case of a triple coinfection. According to to the circulating genotypes, potential vaccine effectiveness was 47% for the 4-valent vaccine and 70% for the 9-valent vaccine.
Conclusion: Within the Cameroonian context, at least one out of five women is likely to be an HR-HPV carrier, especially among young people, smokers, and those with multiple sexual partners. Importantly, HR-HPV infection is highly diversified, with vaccine efficacy ranging from about 47% (4-valent) to 70% (9-valent).
Keywords: Cameroon; HR-HPV; genotype; positivity rate; vaccination.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence, Potential Predictors, and Genotype-Specific Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Infection among Sexually Active Students in Japan.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132462. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26176861 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence and Associated Factors of 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Types among Men in the Multinational HIM Study.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 30;11(11):e0167173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167173. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27902759 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of vaccine and non-vaccine human papillomavirus types among women in Accra and Kumasi, Ghana: a cross-sectional study.BMC Womens Health. 2021 Oct 26;21(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12905-021-01511-1. BMC Womens Health. 2021. PMID: 34702246 Free PMC article.
-
High Prevalence of Anal Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus Infection in Young Men Who Have Sex with Men Living in Bamako, Mali.Infect Agent Cancer. 2021 Jul 1;16(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13027-021-00385-0. Infect Agent Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34210322 Free PMC article.
-
Costs and cost-effectiveness of 9-valent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in two East African countries.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e106836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106836. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25198104 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus genotypes and viral load correlated with squamous cell inflammation among women in Gabon.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Oct 12;24(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03403-6. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39396007 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple human papillomavirus infection and high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions among women with human immunodeficiency virus: a systematic review and a meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 15;11:1403548. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1403548. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39076762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akom E., Venne S., Institut National de Santé Publique du Québec . Institut National de Santé Publique du Québec; 2003. L'infection au virus du papillome humain (VPH)http://www.inspq.qc.ca/publications/defaultlien.asp?E=p&NumPublication=1...
-
- Ali K.E., Mohammed I.A., Difabachew M.N., Demeke D.S., Haile T., Ten Hove R.-J., Kumssa T.H., Woldu Z.L., Haile E.L., Tullu K.D. Burden and genotype distribution of high-risk human papillomavirus infection and cervical cytology abnormalities at selected obstetrics and gynecology clinics of Addis Ababa. Ethiopia. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):768. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5953-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ANSM . Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé; 2006. Mise sur le marché du vaccin pour la prévention d'infections liées au virus papilloma.https://www.ansm.sante.fr/S-informer/Communiques-Communiques-Points-pres...
-
- Apgar B.S., Zoschnick L., Wright T.C. The 2001 Bethesda System terminology. American Family Physician. 2003;68(10):1992–1998. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources