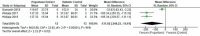Exploring the Potential of Poguntano Extract on Diabetes Management: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36313946
- PMCID: PMC9559780
- DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2022.76.292-296
Exploring the Potential of Poguntano Extract on Diabetes Management: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Poguntano (Picria fel-terrae Merr) is a traditional herb commonly used as a blood glucose lowering agent in Indonesia. However, the effectiveness of the herb has not yet been established.
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to review the hypoglycemic effect of Poguntano extract in lowering plasma glucose levels.
Methods: We conducted a literature search using peer-reviewed databases for relevant articles on Poguntano extract in animal models of diabetes. The effect size was pooled using a random effect model.
Results: Two animal studies were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. There was a significant difference in plasma glucose levels between diabetic control and rats treated with Puguntano extract (MD: 28.77; 95%CI: 6.20-51.34; p=0.01). There was no significant difference between non-diabetic control and Poguntano extract.
Conclusion: Poguntano extract lowers the blood glucose levels in diabetic rats compared to control.
Keywords: Animal; Diabetes Mellitus; Meta-Analysis; Poguntano.
© 2022 Sry Suryani Widjaja, Rusdiana Rusdiana, Lowilius Wiyono.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest in the making of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Aug;9(30):iii-vi, xiii-163. doi: 10.3310/hta9300. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16095545
-
The Effect of Dietary Glycaemic Index on Glycaemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutrients. 2018 Mar 19;10(3):373. doi: 10.3390/nu10030373. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29562676 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for treating foot ulcers, and preventing their recurrence, in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 8;2(2):CD012835. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012835.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 35653236 Free PMC article.
-
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD005060. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005060.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD005060. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005060.pub3. PMID: 15846742 Updated.
References
-
- Bommer C, Sagalova V, Heesemann E, Manne-Goehler J, Atun R, Bärnighausen T, et al. Global Economic Burden of Diabetes in Adults: Projections From 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care. 2018 May;41(5):963–970. - PubMed
-
- Widjaja SS, Rusdiana R. Extract Ethanol of Poguntano in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats [Internet] Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science. 2018;17:251–254. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3329/bjms.v17i2.35879 .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical