A snapshot of protein trafficking in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 36314261
- PMCID: PMC9874443
- DOI: 10.1111/boc.202200073
A snapshot of protein trafficking in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
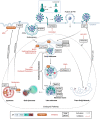
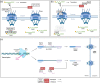
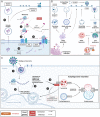
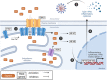
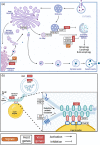
SARS-CoV-2 is a human pathogenic virus responsible for the COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) pandemic. The infection cycle of SARS-CoV-2 involves several related steps, including virus entry, gene expression, RNA replication, assembly of infectious virions and their egress. For all of these steps, the virus relies on and exploits host cell factors, cellular organelles, and processes such as endocytosis, nuclear transport, protein secretion, metabolite transport at membrane contact sites (MSC) and exocytotic pathways. To do this, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved multifunctional viral proteins that hijack cellular factors and modulate their function by unique strategies. In this Review, we highlight cellular trafficking factors, processes, and organelles of relevance to the SARS-CoV-2 infection cycle and how viral proteins make use of and perturb cellular transport during the viral infection cycle.
© 2021 The Authors. Biology of the Cell published by Wiley-VCH GmbH on behalf of Société Française des Microscopies and Société de Biologie Cellulaire de France.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Addetia, A. , Lieberman, N.A.P. , Phung, Q. , Hsiang, T.Y. , Xie, H. , Roychoudhury, P. , Shrestha, L. , Loprieno, M.A. , Huang, M.‐L. , Gale, M. , Jerome, K.R. & Greninger, A.L. (2021) SARS‐CoV‐2 ORF6 disrupts bidirectional nucleocytoplasmic transport through interactions with Rae1 and Nup98. mBio, 12; e0065‐21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, A.K. , Blanco, M.R. , Bruce, E.A. , Honson, D.D. , Chen, L.M. , Chow, A. , Bhat, P. , Ollikainen, N. , Quinodoz, S.A. , Loney, C. , Thai, J. , Miller, Z.D. , Lin, A.E. , Schmidt, M.M. , Stewart, D.G. , Goldfarb, D. , De Lorenzo, G. , Rihn, S.J. , Voorhees, R.M. , Botten, J.W. , Majumdar, D. & Guttman, M. (2020) SARS‐CoV‐2 disrupts splicing, translation, and protein trafficking to suppress host defenses. Cell, 183, 1325‐1339.e21 e1321. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

