Marginal proportional hazards models for clustered interval-censored data with time-dependent covariates
- PMID: 36314377
- PMCID: PMC11971730
- DOI: 10.1111/biom.13787
Marginal proportional hazards models for clustered interval-censored data with time-dependent covariates
Abstract
The Botswana Combination Prevention Project was a cluster-randomized HIV prevention trial whose follow-up period coincided with Botswana's national adoption of a universal test and treat strategy for HIV management. Of interest is whether, and to what extent, this change in policy modified the preventative effects of the study intervention. To address such questions, we adopt a stratified proportional hazards model for clustered interval-censored data with time-dependent covariates and develop a composite expectation maximization algorithm that facilitates estimation of model parameters without placing parametric assumptions on either the baseline hazard functions or the within-cluster dependence structure. We show that the resulting estimators for the regression parameters are consistent and asymptotically normal. We also propose and provide theoretical justification for the use of the profile composite likelihood function to construct a robust sandwich estimator for the variance. We characterize the finite-sample performance and robustness of these estimators through extensive simulation studies. Finally, we conclude by applying this stratified proportional hazards model to a re-analysis of the Botswana Combination Prevention Project, with the national adoption of a universal test and treat strategy now modeled as a time-dependent covariate.
Keywords: HIV; clustered failure time data; composite em algorithm; composite likelihood; interval censoring; marginal models; nonparametric likelihood; proportional hazards; semiparametric regression; time-dependent covariates.
© 2022 The International Biometric Society.
Figures
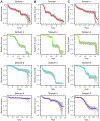
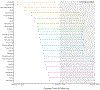
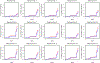
Similar articles
-
Semiparametric regression analysis of partly interval-censored failure time data with application to an AIDS clinical trial.Stat Med. 2021 Sep 10;40(20):4376-4394. doi: 10.1002/sim.9035. Epub 2021 May 26. Stat Med. 2021. PMID: 34080723 Free PMC article.
-
Cox regression for mixed case interval-censored data with covariate errors.Lifetime Data Anal. 2012 Jul;18(3):321-38. doi: 10.1007/s10985-012-9220-x. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Lifetime Data Anal. 2012. PMID: 22447469
-
Marginal proportional hazards models for multivariate interval-censored data.Biometrika. 2023 Sep;110(3):815-830. doi: 10.1093/biomet/asac059. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Biometrika. 2023. PMID: 37601305 Free PMC article.
-
A semiparametric mixture model approach for regression analysis of partly interval-censored data with a cured subgroup.Stat Methods Med Res. 2021 Aug;30(8):1890-1903. doi: 10.1177/09622802211023985. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Stat Methods Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34197261
-
Maximum likelihood estimation for semiparametric transformation models with interval-censored data.Biometrika. 2016 Jun;103(2):253-271. doi: 10.1093/biomet/asw013. Epub 2016 May 24. Biometrika. 2016. PMID: 27279656 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fast standard error estimation for joint models of longitudinal and time-to-event data based on stochastic EM algorithms.Biostatistics. 2024 Dec 31;26(1):kxae043. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxae043. Biostatistics. 2024. PMID: 39523821
References
-
- Cai T, Wei LJ, and Wilcox M (2000). Semiparametric regression analysis for clustered failure time data. Biometrika 87, 867–878.
-
- Chandler RE and Bate S (2007). Inference for clustered data using the independence loglikelihood. Biometrika 94, 167–183.
-
- Chen M-H, Tong X, and Zhu L (2013). A linear transformation model for multivariate interval-censored failure time data. Canadian Journal of Statistics 41, 275–290.
-
- Cook RJ and Tolusso D (2009). Second-order estimating equations for the analysis of clustered current status data. Biostatistics 10, 756–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

