The impact of bariatric surgery procedures on the modulation of cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with severe obesity: a 12-month follow-up
- PMID: 36314880
- PMCID: PMC9629577
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605221119657
The impact of bariatric surgery procedures on the modulation of cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with severe obesity: a 12-month follow-up
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of one anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB), Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), and sleeve gastrectomy (SG) on cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs) in patients with severe obesity.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients with severe obesity who had undergone OAGB, RYGB, or SG between 2015 and 2017 and follow-up assessments over 12-months.
Results: Among 485 included patients, anthropometric measurements, body composition, fasting blood glucose (FBG), lipid profile, and comorbidities were significantly improved for all three procedures throughout the follow-up period. Weight, % total weight loss (%TWL), body mass index, fat mass and fat mass to fat-free mass ratio improvements were higher with RYGB and OAGB than SG. There were no significant differences between procedures in all other variables. A significant trend toward remission rate of dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus was observed with all three procedures, with no significant difference between the three groups. %TWL statistically correlated with fat mass, FBG, and triglycerides.
Conclusions: OAGB, RYGB, and SG had a beneficial impact on CMRFs and comorbidities during 12 months of follow-up. Of note, RYGB and OAGB may result in better outcomes, particularly anthropometric and body composition indices. Further large-sample, long-term follow-up studies are required to expand on the present findings.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; comorbidities; dyslipidemia; obesity; type 2 diabetes mellitus; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
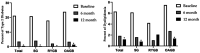
Similar articles
-
Long-term follow-up after sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus one-anastomosis gastric bypass: a prospective randomized comparative study of weight loss and remission of comorbidities.Surg Endosc. 2019 Feb;33(2):401-410. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6307-9. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Surg Endosc. 2019. Retraction in: Surg Endosc. 2021 Mar;35(3):1492. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08298-0. PMID: 29943058 Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Weight Loss Results, Remission of Comorbidities and Nutritional Deficiencies of Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG), Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) on Type 2 Diabetic (T2D) Patients.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 20;17(20):7644. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17207644. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33092117 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of single-anastomosis gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy on type 2 diabetes mellitus remission for obese patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Asian J Surg. 2023 Oct;46(10):4152-4160. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2023.03.062. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Asian J Surg. 2023. PMID: 37002039 Review.
-
Long-Term Efficacy of Bariatric Surgery for the Treatment of Super-Obesity: Comparison of SG, RYGB, and OAGB.Obes Surg. 2021 Aug;31(8):3391-3399. doi: 10.1007/s11695-021-05464-0. Epub 2021 May 16. Obes Surg. 2021. PMID: 33993423
-
Efficiency and safety of single anastomosis sleeve ileal (SASI) bypass in the treatment of obesity and associated comorbidities: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2024 Jul 18;409(1):221. doi: 10.1007/s00423-024-03413-w. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2024. PMID: 39023536 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A multifaceted and inclusive methodology for the detection of sarcopenia in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: an in-depth analysis of current evidence.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024 Aug;25(4):677-689. doi: 10.1007/s11154-023-09864-8. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 38427134 Review.
-
Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) after Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG), One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB), and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB): A Systematic Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 19;59(5):985. doi: 10.3390/medicina59050985. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241216 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and Long-Term Impact of Metabolic Surgery on Obesity Outcomes in Iranian Non-Diabetic Obese Patients.Maedica (Bucur). 2025 Jun;20(2):209-219. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2025.20.2.209. Maedica (Bucur). 2025. PMID: 40880689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gómez-Ambrosi J, Moncada R, Valentí V, et al. Cardiometabolic profile related to body adiposity identifies patients eligible for bariatric surgery more accurately than BMI. Obes Surg 2015; 25: 1594–1603. - PubMed
-
- Hasani M, Mirahmadian M, Taheri E, et al. The effect of laparoscopic gastric plication surgery on body composition, resting energy expenditure, thyroid hormones, and physical activity in morbidly obese patients. Bariatric Surgical Practice and Patient Care 2015; 10: 173–179.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

