SARS-CoV-2: Challenges in Reconverting Diagnostic Laboratories to Combat the Pandemic
- PMID: 36314981
- PMCID: PMC9769709
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01477-22
SARS-CoV-2: Challenges in Reconverting Diagnostic Laboratories to Combat the Pandemic
Abstract
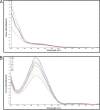
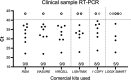
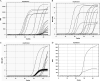
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first detected in Mexico in February 2020. Even though health authorities did not perceive then the value of viral detection tests, we anticipated the demand for them. We set up to develop an expeditious severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) molecular diagnostic service through the implementation of standardized protocols for biospecimen sampling, transportation, biobanking, preanalytical validation, and nucleic acids (NA) testing (NAT). Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs collected in a special transportation medium were the biospecimens from which NAs were purified either manually or automatically. Viral RNA genome presence was determined using commercial SARS-CoV-2 detection kits (based on reverse transcription coupled with real-time PCR [RT-PCR]). Improvements in laboratory processing speed and reliability resulted from semi-automatizing laboratory processes and adopting a quality control/quality assurance system (QC/QA), respectively. NAs that were purified, either manually or automatically, were validated by preanalytical spectrophotometric characterization. Automated purification was less prone to contamination and reduced the processing time. The following six RT-PCR kits were evaluated for their convenience, specificity, sensitivity, time consumption, and required materials (in order, starting with the kit with the best results): RIDA gene and Viasure (tied), Vircell, LightMix, 1copy, and Logix Smart. Redesigning the laboratories' working areas, equipment, fluxes of personnel and material, and personnel skills, and overemphasizing biosafety safeguards were major challenges encountered in the middle of the sanitary crisis. Adopting a QC/QA system, utilizing automatization processes, and working closely with health authorities were key factors in our success. IMPORTANCE Rearranging our diagnostic laboratories to improve the fight against a new unexpected, unpredictable, and sudden public health threat demanded that we move quickly to redesign not only the laboratory processes but also the distribution of space, personnel activities, and fluxes of material coming in and out. We also had to work closely with governmental health authorities to gain their trust in our technical competence. Gaining the confidence of the clients, i.e., mainly individuals, the human resource departments of factories and corporations sending employees for testing, and medical institutions, and implementing as much automatization as possible of processes, in which only officially approved reagents (for extraction and analysis of NA) were used to generate opportune trustable testing results, were key factors. Our laboratories have gathered a considerable amount of experience and significant number of solutions, considering our geographic contexts alongside this continuously morphing pandemic, validating many techniques that might help other laboratories find a better and more precise workflow.
Keywords: RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis; commercial RT-PCR kits; laboratory techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Standardization of SARS-CoV-2 Cycle Threshold Values: Multisite Investigation Evaluating Viral Quantitation across Multiple Commercial COVID-19 Detection Platforms.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0447022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04470-22. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36651781 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Various Alternative Economical and High Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Testing Methods within Resource-Limited Settings.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14350. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214350. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430827 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study on the efficiency of commercial reverse transcriptase-Polymerase chain reaction kits for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections.Indian J Public Health. 2022 Jul-Sep;66(3):276-281. doi: 10.4103/ijph.ijph_2042_21. Indian J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36149104
-
Steps, implementation and importance of quality management in diagnostic laboratories with special emphasis on coronavirus disease-2019.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jul-Dec;38(3 & 4):243-251. doi: 10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_20_353. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33154231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding, Verifying, and Implementing Emergency Use Authorization Molecular Diagnostics for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Jul 23;58(8):e00796-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00796-20. Print 2020 Jul 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32381642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Hypertonic Seawater Nasal Irrigation Solution Containing Algal and Herbal Natural Ingredients Reduces Viral Load and SARS-CoV-2 Detection Time in the Nasal Cavity.J Pers Med. 2023 Jul 3;13(7):1093. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071093. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai C-C, Liu YH, Wang C-Y, Wang Y-H, Hsueh S-C, Yen M-Y, Ko W-C, Hsueh P-R. 2020. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): facts and myths. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 53:404–412. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malik YA. 2020. Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Malays J Pathol 42:3–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

