The central scaffold protein CEP350 coordinates centriole length, stability, and maturation
- PMID: 36315013
- PMCID: PMC9623370
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202203081
The central scaffold protein CEP350 coordinates centriole length, stability, and maturation
Abstract
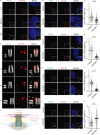
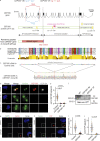
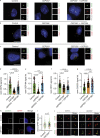
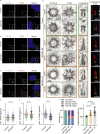
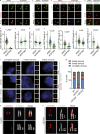
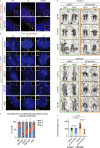
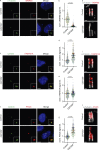
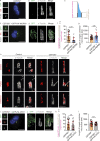
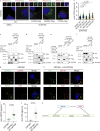
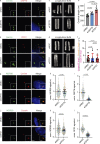
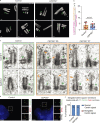
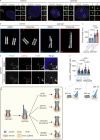
The centriole is the microtubule-based backbone that ensures integrity, function, and cell cycle-dependent duplication of centrosomes. Mostly unclear mechanisms control structural integrity of centrioles. Here, we show that the centrosome protein CEP350 functions as scaffold that coordinates distal-end properties of centrioles such as length, stability, and formation of distal and subdistal appendages. CEP350 fulfills these diverse functions by ensuring centriolar localization of WDR90, recruiting the proteins CEP78 and OFD1 to the distal end of centrioles and promoting the assembly of subdistal appendages that have a role in removing the daughter-specific protein Centrobin. The CEP350-FOP complex in association with CEP78 or OFD1 controls centriole microtubule length. Centrobin safeguards centriole distal end stability, especially in the compromised CEP350-/- cells, while the CEP350-FOP-WDR90 axis secures centriole integrity. This study identifies CEP350 as a guardian of the distal-end region of centrioles without having an impact on the proximal PCM part.
© 2022 Karasu et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
WDR90 is a centriolar microtubule wall protein important for centriole architecture integrity.Elife. 2020 Sep 18;9:e57205. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57205. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32946374 Free PMC article.
-
CEP19 cooperates with FOP and CEP350 to drive early steps in the ciliogenesis programme.Open Biol. 2017 Jun;7(6):170114. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170114. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28659385 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1 controls centriole distal appendage formation and centrobin removal via independent pathways.J Cell Sci. 2022 Apr 15;135(8):jcs259120. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259120. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 35343570
-
Structure and function of distal and subdistal appendages of the mother centriole.J Cell Sci. 2023 Feb 1;136(3):jcs260560. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260560. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 36727648 Review.
-
Accessorizing the centrosome: new insights into centriolar appendages and satellites.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Feb;66:148-155. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.10.021. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 33279729 Review.
Cited by
-
A disease-associated PPP2R3C-MAP3K1 phospho-regulatory module controls centrosome function.Curr Biol. 2024 Oct 21;34(20):4824-4834.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.08.058. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 39317195
-
An interaction network of inner centriole proteins organised by POC1A-POC1B heterodimer crosslinks ensures centriolar integrity.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 14;15(1):9857. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54247-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39543170 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting potential target genes in molecular biology experiments using machine learning and multifaceted data sources.iScience. 2024 Feb 23;27(3):109309. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109309. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38482491 Free PMC article.
-
Interactome Analysis Reveals a Link of the Novel ALMS1-CEP70 Complex to Centrosomal Clusters.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024 Jan;23(1):100701. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100701. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38122899 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM37 employs peptide motif recognition and substrate-dependent oligomerization to prevent ectopic spindle pole assembly.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 9:2024.10.09.617493. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.09.617493. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 May 25. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01562-0. PMID: 39416052 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

