From oncoproteins to spike proteins: the evaluation of intramolecular stability using hydropathic force field
- PMID: 36315295
- PMCID: PMC9628575
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-022-00477-y
From oncoproteins to spike proteins: the evaluation of intramolecular stability using hydropathic force field
Abstract
Evaluation of the intramolecular stability of proteins plays a key role in the comprehension of their biological behavior and mechanism of action. Small structural alterations such as mutations induced by single nucleotide polymorphism can impact biological activity and pharmacological modulation. Covid-19 mutations, that affect viral replication and the susceptibility to antibody neutralization, and the action of antiviral drugs, are just one example. In this work, the intramolecular stability of mutated proteins, like Spike glycoprotein and its complexes with the human target, is evaluated through hydropathic intramolecular energy scoring originally conceived by Abraham and Kellogg based on the "Extension of the fragment method to calculate amino acid zwitterion and side-chain partition coefficients" by Abraham and Leo in Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 1987, 2:130 - 52. HINT is proposed as a fast and reliable tool for the stability evaluation of any mutated system. This work has been written in honor of Prof. Donald J. Abraham (1936-2021).
Keywords: Intramolecular stability; LogPo/w; Mutations; Scoring function.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures


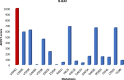

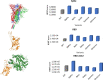
References
-
- Anfinsen CB (1973) “Principles that Govern the Folding of Protein Chains,” Science (1979), vol. 181, no. 4096, pp. 223–230, Jul. 10.1126/science.181.4096.223 - PubMed
-
- Bryngelson JD, Onuchic JN, Socci ND, Wolynes PG (1995) “Funnels, pathways, and the energy landscape of protein folding: A synthesis,” Proteins: Structure, Function, and Genetics, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 167–195, Mar. 10.1002/prot.340210302 - PubMed
-
- Godoy-Ruiz R, Perez-Jimenez R, Ibarra-Molero B, Sanchez-Ruiz JM (Feb. 2004) Relation Between Protein Stability, Evolution and Structure, as Probed by Carboxylic Acid Mutations. J Mol Biol 336(2):313–318. 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.048 - PubMed
-
- Goldstein RA (2011) “The evolution and evolutionary consequences of marginal thermostability in proteins,” Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, vol. 79, no. 5, pp. 1396–1407, May 10.1002/prot.22964 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

