Translational buffering by ribosome stalling in upstream open reading frames
- PMID: 36315596
- PMCID: PMC9648851
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010460
Translational buffering by ribosome stalling in upstream open reading frames
Abstract
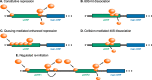
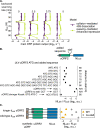
Upstream open reading frames (uORFs) are present in over half of all human mRNAs. uORFs can potently regulate the translation of downstream open reading frames through several mechanisms: siphoning away scanning ribosomes, regulating re-initiation, and allowing interactions between scanning and elongating ribosomes. However, the consequences of these different mechanisms for the regulation of protein expression remain incompletely understood. Here, we performed systematic measurements on the uORF-containing 5' UTR of the cytomegaloviral UL4 mRNA to test alternative models of uORF-mediated regulation in human cells. We find that a terminal diproline-dependent elongating ribosome stall in the UL4 uORF prevents decreases in main ORF protein expression when ribosome loading onto the mRNA is reduced. This uORF-mediated buffering is insensitive to the location of the ribosome stall along the uORF. Computational kinetic modeling based on our measurements suggests that scanning ribosomes dissociate rather than queue when they collide with stalled elongating ribosomes within the UL4 uORF. We identify several human uORFs that repress main ORF protein expression via a similar terminal diproline motif. We propose that ribosome stalls in uORFs provide a general mechanism for buffering against reductions in main ORF translation during stress and developmental transitions.
Copyright: © 2022 Bottorff et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Johnstone TG, Bazzini AA, Giraldez AJ. Upstream ORFs are prevalent translational repressors in vertebrates. The EMBO Journal [Internet]. 2016. Apr 1 [cited 2020 Nov 20];35(7):706–23. Available from: https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/embj.201592759 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

