Intravenous injection of a novel viral immunotherapy encoding human interleukin-7 in nonhuman primates is safe and increases absolute lymphocyte count
- PMID: 36315906
- PMCID: PMC9746448
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2133914
Intravenous injection of a novel viral immunotherapy encoding human interleukin-7 in nonhuman primates is safe and increases absolute lymphocyte count
Abstract
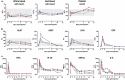
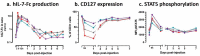
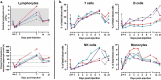
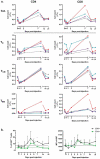
Persistence of an immunosuppression, affecting both the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system, plays a role in sepsis patients' morbidity and late mortality pointing to the need for broad and effective immune interventions. MVA-hIL-7-Fc is a non-replicative recombinant Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara encoding the human interleukin-7 fused to human IgG2 Fc fragment. We have shown in murine sepsis models the capacity of this new virotherapy to stimulate both arms of the immune system and increase survival. Herein, an exploratory study in nonhuman primates was performed following a single intravenous injection of the MVA-hIL-7-Fc used at the clinical dose to assess its safety and biological activities. Four cynomolgus macaques were followed for 3 weeks post-injection (p.i), without observed acute adverse reactions. Circulating hIL-7-Fc was detected during the first 3-5 days p.i with a detection peaking at 12 h p.i. IL-7 receptor engagement and downstream signal transduction were detected in T cells demonstrating functionality of the expressed IL-7. Expansion of blood lymphocytes, mainly CD4 and CD8 naïve and central memory T cells, was observed on day 7 p.i. together with a transient increase of Ki67 expression on T lymphocytes. In addition, we observed an increase in circulating B and NK cells as well as monocytes were albeit with different kinetics and levels. This study indicates that a vectorized IL-7-Fc, injected by intravenous route at a relevant clinical dose in a large animal model, is active without adverse reactions supporting the clinical development of this novel virotherapy for treatment of sepsis patients.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara; immune activation; interleukin-7; nonhuman primates; pharmacokinetics; virotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-7 producing immunotherapy improves ex vivo T cell functions of immunosenescent patients, especially post hip fracture.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2232247. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2232247. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37417353 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Delivery of IL-7 Is a Potent Immunotherapy Stimulating Innate and Adaptive Immunity and Confers Survival in Sepsis Models.J Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;209(1):99-117. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101145. Epub 2022 Jun 6. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35667841
-
A novel virotherapy encoding human interleukin-7 improves ex vivo T lymphocyte functions in immunosuppressed patients with septic shock and critically ill COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:939899. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.939899. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045686 Free PMC article.
-
Modified vaccinia virus Ankara encoding influenza virus hemagglutinin induces heterosubtypic immunity in macaques.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(22):13418-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01219-14. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25210172 Free PMC article.
-
[Novel vaccines against M. tuberculosis].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):745-51. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240920 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The pathophysiology of sepsis and precision-medicine-based immunotherapy.Nat Immunol. 2024 Jan;25(1):19-28. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01660-5. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38168953 Review.
-
IL-7 producing immunotherapy improves ex vivo T cell functions of immunosenescent patients, especially post hip fracture.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2232247. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2232247. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37417353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fry TJ, Moniuszko M, Creekmore S, Donohue SJ, Douek DC, Giardina S, Hecht TT, Hill BJ, Komschlies K, Tomaszewski J, et al. IL-7 therapy dramatically alters peripheral T-cell homeostasis in normal and SIV-infected nonhuman primates. Blood. 2003;101(6):2294–99. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-07-2297. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park J-H, Yu Q, Erman B, Appelbaum JS, Montoya-Durango D, Grimes HL, Singer A. Suppression of IL7Ralpha transcription by IL-7 and other prosurvival cytokines: a novel mechanism for maximizing IL-7-dependent T cell survival. Immunity. 2004;21(2):289–302. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
