Conformationally Defined Rexinoids for the Prevention of Inflammation and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers
- PMID: 36318154
- PMCID: PMC9942614
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00735
Conformationally Defined Rexinoids for the Prevention of Inflammation and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers
Abstract
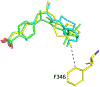
Compound 1 is a potent rexinoid that is highly effective in cancer chemoprevention but elevates serum triglycerides. In an effort to separate the lipid toxicity from the anticancer activity of 1, we synthesized four new analogs of rexinoid 1, of which three rexinoids did not elevate serum triglycerides. Rexinoids 3 and 4 are twice as potent as rexinoid 1 in binding to Retinoid X receptor (RXR). All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) plays a key role in maintaining skin homeostasis, and rexinoids 3-6 are highly effective in upregulating the genes responsible for the biosynthesis of ATRA. Inflammation plays a key role in skin cancer, and rexinoids 3 and 4 are highly effective in diminishing LPS-induced inflammation. Rexinoids 3 and 4 are highly effective in preventing UVB-induced nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) without displaying any overt toxicities. Biophysical studies of rexinoids 3 and 5 bound to hRXRα-ligand binding domain (LBD) reveal important conformational and dynamical differences in the ligand binding domain.
Figures
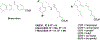


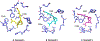



Similar articles
-
The "Phantom Effect" of the Rexinoid LG100754: structural and functional insights.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e15119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015119. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21152046 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation retinoid X receptor agonists increase ATRA signaling in organotypic epithelium cultures and have distinct effects on receptor dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jan;299(1):102746. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102746. Epub 2022 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36436565 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the communication between agonist and coactivator binding in the retinoid X receptor α ligand binding domain.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 10;289(2):814-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476861. Epub 2013 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24187139 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of RXR function through ligand design.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1821(1):57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.04.003. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21515403 Review.
-
Retinoic Acid and Its Derivatives in Skin.Cells. 2020 Dec 11;9(12):2660. doi: 10.3390/cells9122660. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33322246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoid X Receptor agonists as selective modulators of the immune system for the treatment of cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Dec;252:108561. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108561. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37952906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoid X Receptor Activation Prevents Diabetic Retinopathy in Murine Models.Cells. 2023 Sep 26;12(19):2361. doi: 10.3390/cells12192361. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830574 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: a double-edged sword in cancer development and therapy.Mol Biomed. 2024 Oct 17;5(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00209-8. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39417901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 22;26(9):3933. doi: 10.3390/ijms26093933. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willems S; Zaienne D; Merk D Targeting nuclear receptors in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. J. Med. Chem 2021, 64, 9592–9638. - PubMed
-
- Dheer Y; Chitranshi N; Gupta V; Sharma S; Pushpitha K; Abbasi M; Mirzaei M; You Y; Graham SL; Gupta V Retinoid x receptor modulation protects against ER stress response and rescues glaucoma phenotypes in adult mice. Exp. Neurol 2019, 314, 111–125. - PubMed
-
- Duvic M; Martin AG; Kim Y; Olsen E; Wood GS; Crowley CA; Yocum RC; Worldwide Bexarotene Study Group. Phase 2 and 3 clinical trial of oral bexarotene (targretin capsules) for the treatment of refractory or persistent early-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch. Dermatol 2001, 137, 581–593. - PubMed
-
- Assaf C; Bagot M; Dummer R; Duvic M; Gniadecki R; Knobler R; Ranki A; Schwandt P; Whittaker S Minimizing adverse side-effects of oral bexarotene in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: an expert opinion. Br. J. Dermatol 2006, 155, 261–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

