Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Momordica Saponin II Derivatives as Vaccine Adjuvants
- PMID: 36318612
- PMCID: PMC10202417
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01087
Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Momordica Saponin II Derivatives as Vaccine Adjuvants
Abstract
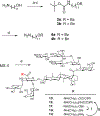
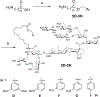
VSA-2 is a recently developed semisynthetic saponin immunostimulant. It is prepared by incorporating a terminal-functionalized side chain to the branched trisaccharide domain at the C3 position of Momordica saponin II (MS II) isolated from the seeds of perennial Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng. Direct comparison of VSA-2 and the clinically proven saponin adjuvant QS-21 shows that VSA-2 is comparable to QS-21 in enhancing humoral and cellular immune responses. Structure-activity relationship studies show that structural changes in the side chain have a significant impact on saponins' adjuvant activity. However, with the VSA-2 molecular framework intact, the new VSA-2 analogues with various substitution(s) at the terminal benzyl group of the side chain retain the ability of potentiating antigen-specific humoral and cellular responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): P.W. is inventor on patent applications partially based on this work. P.W. and S.M. are co-founders of Adjuvax, LLC.
Figures

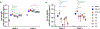


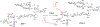
Similar articles
-
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants.Med Chem Res. 2024;33(8):1292-1306. doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03227-x. Epub 2024 May 18. Med Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 39132259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccine Adjuvants Derivatized from Momordica Saponins I and II.J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 14;62(21):9976-9982. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01511. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31657920 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiating pneumococcal glycoconjugate vaccine PCV13 with saponin adjuvant VSA-1.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 12;13:1079047. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079047. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36578488 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Effect on Adjuvanticity of Saponins.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 26;63(6):3290-3297. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02063. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32101001 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of immunostimulatory saponins: A sweet challenge for carbohydrate chemists.Carbohydr Res. 2023 Aug;530:108851. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2023.108851. Epub 2023 May 23. Carbohydr Res. 2023. PMID: 37257206 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants.Med Chem Res. 2024;33(8):1292-1306. doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03227-x. Epub 2024 May 18. Med Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 39132259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kensil CR; Mo AX; Truneh A Current vaccine adjuvants: An overview of a diverse class. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2972–2988. - PubMed
-
- Leroux-Roels G Unmet needs in modern vaccinology: adjuvants to improve the immune response. Vaccine 2010, 28, C25–C36. - PubMed
-
- Sharp FA; Lavelle EC Discovery of vaccine adjuvants. In Development of Therapeutic Agents Handbook, 1st ed.; Gad SC, Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, 2012; pp 533–546.
-
- Wang W; Singh M Selection of adjuvants for enhanced vaccine potency. World J. Vaccine 2011, 01, 33–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

