WNK kinases sense molecular crowding and rescue cell volume via phase separation
- PMID: 36318922
- PMCID: PMC9699283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.042
WNK kinases sense molecular crowding and rescue cell volume via phase separation
Abstract
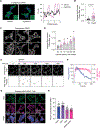
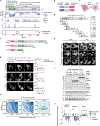
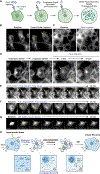
When challenged by hypertonicity, dehydrated cells must recover their volume to survive. This process requires the phosphorylation-dependent regulation of SLC12 cation chloride transporters by WNK kinases, but how these kinases are activated by cell shrinkage remains unknown. Within seconds of cell exposure to hypertonicity, WNK1 concentrates into membraneless condensates, initiating a phosphorylation-dependent signal that drives net ion influx via the SLC12 cotransporters to restore cell volume. WNK1 condensate formation is driven by its intrinsically disordered C terminus, whose evolutionarily conserved signatures are necessary for efficient phase separation and volume recovery. This disorder-encoded phase behavior occurs within physiological constraints and is activated in vivo by molecular crowding rather than changes in cell size. This allows kinase activity despite an inhibitory ionic milieu and permits cell volume recovery through condensate-mediated signal amplification. Thus, WNK kinases are physiological crowding sensors that phase separate to coordinate a cell volume rescue response.
Keywords: K-Cl cotransport; Na-K-2Cl cotransport; SLC12 cotransporter; WNK kinase; biomolecular condensates; cell volume regulation; hyperosmotic stress; macromolecular crowding; phase separation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Controlling the crowd with a WNK.Cell. 2022 Nov 23;185(24):4465-4467. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.027. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36423576 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 BX002891/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- S10 OD021627/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028596/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS098379/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS086749/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119252/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS105756/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 DK119180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005647/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK110358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK118211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL155777/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

