Biological Characteristics of Recombinant Arthrobotrys oligospora Chitinase AO-801
- PMID: 36320111
- PMCID: PMC9633153
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2022.60.5.345
Biological Characteristics of Recombinant Arthrobotrys oligospora Chitinase AO-801
Abstract
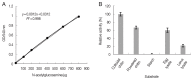
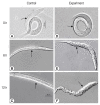
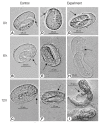
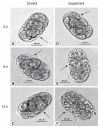
Chitinase AO-801 is a hydrolase secreted by Arthrobotrys oligospora during nematode feeding, while its role remained elusive. This study analyzed the molecular characteristics of recombinant chitinase of Arthrobotrys oligospora (reAO-801). AO-801 belongs to the typical glycoside hydrolase 18 family with conserved chitinase sequence and tertiary structure of (α/β)8 triose-phosphate isomerase (TIM) barrel. The molecular weight of reAO-801 was 42 kDa. reAO-801 effectively degraded colloidal and powdered chitin, egg lysate, and stage I larval lysate of Caenorhabditis elegans. The activity of reAO-801 reached its peak at 40˚C and pH values between 4-7. Enzyme activity was inhibited by Zn2+, Ca2+, and Fe3+, whereas Mg2+ and K+ potentiated its activity. In addition, urea, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and 2-mercaptoethanol significantly inhibited enzyme activity. reAO-801 showed complete nematicidal activity against C. elegans stage I larvae. reAO-801 broke down the C. elegans egg shells, causing them to die or die prematurely by hatching the eggs. It also invoked degradation of Haemonchus contortus eggs, resulting in apparent changes in the morphological structure. This study demonstrated the cytotoxic effect of reAO-801, which laid the foundation for further dissecting the mechanism of nematode infestation by A. oligospora.
Keywords: Arthrobotrys oligospora; biological activity; chitinase; enzyme characteristic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteomic insights into nematode-trapping fungi Arthrobotrys oligospora after their response to chitin.J Vet Res. 2025 Feb 25;69(1):71-82. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2025-0005. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40144063 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional analyses of the chitinase-encoding genes in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora.Arch Microbiol. 2013 Jul;195(7):453-62. doi: 10.1007/s00203-013-0894-6. Epub 2013 May 10. Arch Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23661195
-
The recombinant serine protease XAoz1 of Arthrobotrys oligospora exhibits potent nematicidal activity against Caenorhabditis elegans and Haemonchus contortus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013 Jul;344(1):53-9. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12154. Epub 2013 May 13. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23574378
-
Expression of serine proteinase P186 of Arthrobotrys oligospora and analysis of its nematode-degrading activity.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015 Dec;108(6):1485-1494. doi: 10.1007/s10482-015-0595-z. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015. PMID: 26419902
-
Predator-prey interactions of nematode-trapping fungi and nematodes: both sides of the coin.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 May;102(9):3939-3949. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8897-5. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29523933 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review on products derived from nematophagous fungi in the biological control of parasitic helminths of animals.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 1;40(7):224. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04036-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38822201
-
Expression profiles and characterization of microRNAs responding to chitin in Arthrobotrys oligospora.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;206(5):220. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03949-x. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38630188
-
Proteomic insights into nematode-trapping fungi Arthrobotrys oligospora after their response to chitin.J Vet Res. 2025 Feb 25;69(1):71-82. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2025-0005. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40144063 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

