Delivery strategies for CRISPR/Cas genome editing tool for retinal dystrophies: challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 36320315
- PMCID: PMC9614410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.02.001
Delivery strategies for CRISPR/Cas genome editing tool for retinal dystrophies: challenges and opportunities
Abstract
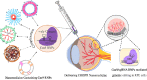
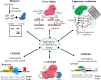
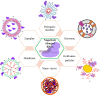
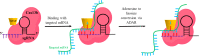
CRISPR/Cas, an adaptive immune system in bacteria, has been adopted as an efficient and precise tool for site-specific gene editing with potential therapeutic opportunities. It has been explored for a variety of applications, including gene modulation, epigenome editing, diagnosis, mRNA editing, etc. It has found applications in retinal dystrophic conditions including progressive cone and cone-rod dystrophies, congenital stationary night blindness, X-linked juvenile retinoschisis, retinitis pigmentosa, age-related macular degeneration, leber's congenital amaurosis, etc. Most of the therapies for retinal dystrophic conditions work by regressing symptoms instead of reversing the gene mutations. CRISPR/Cas9 through indel could impart beneficial effects in the reversal of gene mutations in dystrophic conditions. Recent research has also consolidated on the approaches of using CRISPR systems for retinal dystrophies but their delivery to the posterior part of the eye is a major concern due to high molecular weight, negative charge, and in vivo stability of CRISPR components. Recently, non-viral vectors have gained interest due to their potential in tissue-specific nucleic acid (miRNA/siRNA/CRISPR) delivery. This review highlights the opportunities of retinal dystrophies management using CRISPR/Cas nanomedicine.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Gene editing; Non-viral nanocarriers; Retinal dystrophies.
© 2022 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene editing prospects for treating inherited retinal diseases.J Med Genet. 2020 Jul;57(7):437-444. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106473. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 31857428 Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Gene Activation as a Versatile Tool for Treatment of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1468:95-99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-76550-6_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39930179 Review.
-
CRISPR Cas9 based genome editing in inherited retinal dystrophies.Ophthalmic Genet. 2021 Aug;42(4):365-374. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2021.1904421. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Ophthalmic Genet. 2021. PMID: 33821751 Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-A Promising Therapeutic Tool to Cure Blindness: Current Scenario and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11482. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911482. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular delivery of CRISPR/Cas genome editing components for treatment of eye diseases.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jan;168:181-195. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.011. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 32603815 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and in silico analysis of a spectrum of SLC4A11 variations in Indian familial and sporadic cases of congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Sep 17;17(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02521-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36115991 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances and prospects of nanoparticle-based drug delivery for diabetic ocular complications.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 25;15(8):3551-3570. doi: 10.7150/thno.108691. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40093887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanovesicular Drug Delivery Systems for Rare Ocular Diseases: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jul 23;26(7):197. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03159-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40702295 Review.
-
Inhibition of METTL14 overcomes CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance driven by METTL14-m6A-E2F1-axis in ERα-positive breast cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jan 3;23(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03021-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39754249 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 as a Mutagenic Factor.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):823. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020823. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Samson J.E., Magadan A.H., Sabri M., Moineau S. Revenge of the phages: defeating bacterial defences. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:675–687. - PubMed
-
- Sahel D.K., Mittal A., Chitkara D. CRISPR/Cas system for genome editing: progress and prospects as a therapeutic tool. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370:725–735. - PubMed
-
- Mojica F.J.M., Diez-Villasenor C., Garcia-Martinez J., Almendros C. Short motif sequences determine the targets of the prokaryotic CRISPR defence system. Microbiology (Reading, Engl.) 2009;155:733–740. - PubMed
-
- Zhan T., Rindtorff N., Betge J., Ebert M.P., Boutros M. CRISPR/Cas9 for cancer research and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;55:106–119. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

