Primary Metabolite Chromatographic Profiling as a Tool for Chemotaxonomic Classification of Seeds from Berry Fruits
- PMID: 36320360
- PMCID: PMC9590267
- DOI: 10.17113/ftb.60.03.22.7505
Primary Metabolite Chromatographic Profiling as a Tool for Chemotaxonomic Classification of Seeds from Berry Fruits
Abstract
Research background: Considering the importance of consumption of berry fruits with proven health-beneficial properties and difficulties in quality control of products of specific botanical and geographic origin, a fingerprint method was developed, based on advanced data analysis (pattern recognition, classification), in order to relate the variability of nutrients in the selected cultivars to primary metabolite profile.
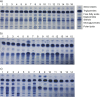
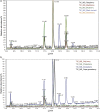
Experimental approach: Forty-five samples of genuine berry fruit cultivars (strawberry, raspberry, blackberry, black currant, blueberry, gooseberry, chokeberry, cape gooseberry and goji berry) were characterized according to chromatographic profiles of primary metabolites (sugars, lipids and fatty acids) obtained by three chromatographic techniques (high-performance thin-layer chromatography, gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry, and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection).
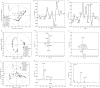
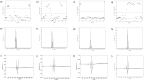
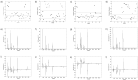
Results and conclusions: Comprehensive analysis allowed monitoring and identification of metabolites belonging to polar lipids, mono-, di- and triacylglycerols, free fatty acids, free sterols, sterol esters, mono- to heptasaccharides and sugar alcohols. Chemical fingerprint of berry seeds showed the uniformity of primary metabolites within each fruit species, but revealed differences depending on the botanical origin. All three chromatographic methods provided a discriminative, informative and predictive metabolomics methodology, which proved to be useful for chemotaxonomic classification.
Novelty and scientific contribution: A novel methodology for the identification of bioactive compounds from primary metabolites of natural products was described. The proposed untargeted metabolite profiling approach could be used in the future as a routine method for tracing of novel bioactive compounds. The knowledge of metabolite composition obtained in this study can provide a better assessment of genotypic and phenotypic differences between berry fruit species and varieties, and could contribute to the development of new breeding programs.
Keywords: berry seeds; chemical fingerprint; chromatography techniques; sugar, lipid and fatty acid identification.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Singh R. Chemotaxonomy: A tool for plant classification. Faslnamah-i Giyahan-i Daruyi. 2016;4(2):90–3.
-
- Pan Z, Li Y, Deng X, Xiao S. Non-targeted metabolomic analysis of orange (Citrus sinensis [L.] Osbeck) wild type and bud mutant fruits by direct analysis in real-time and HPLC-electrospray mass spectrometry. Metabolomics. 2014;10(3):508–23. 10.1007/s11306-013-0597-7 - DOI
-
- Santucci C, Brizzolara S, Tenori L. Comparison of frozen and fresh apple pulp for NMR-based metabolomic analysis. Food Anal Methods. 2015;8(8):2135–40. 10.1007/s12161-015-0107-9 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
