Induction immunosuppression and outcome in kidney transplant recipients with early COVID-19 after transplantation
- PMID: 36320365
- PMCID: PMC9129170
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac112
Induction immunosuppression and outcome in kidney transplant recipients with early COVID-19 after transplantation
Abstract
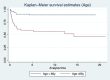
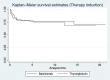
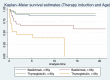
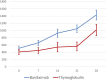
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in kidney transplant recipients has a high risk of complications and mortality, especially in older recipients diagnosed during the early period after transplantation. Management of immunosuppression has been challenging during the pandemic. We investigated the impact of induction immunosuppression, either basiliximab or thymoglobulin, on the clinical evolution of kidney transplant recipients developing COVID-19 during the early period after transplantation. We included kidney transplant recipients with ˂6 months with a functioning graft diagnosed with COVID-19 from the initial pandemic outbreak (March 2020) until 31 July 2021 from different Spanish centres participating in a nationwide registry. A total of 127 patients from 17 Spanish centres developed COVID-19 during the first 6 months after transplantation; 73 (57.5%) received basiliximab and 54 (42.5%) thymoglobulin. Demographics were not different between groups but patients receiving thymoglobulin were more sensitized [calculated panel reactive antibodies (cPRAs) 32.7 ± 40.8% versus 5.6 ± 18.5%] and were more frequently retransplants (30% versus 4%). Recipients ˃65 years of age treated with thymoglobulin showed the highest rate of acute respiratory distress syndrome [64.7% versus 37.1% for older recipients receiving thymoglobulin and basiliximab (P < .05), respectively, and 23.7% and 18.9% for young recipients receiving basiliximab and thymoglobulin (P > .05)], respectively, and the poorest survival [mortality rate 64.7% and 42.9% for older recipients treated with thymoglobulin and basiliximab, respectively (P < .05) and 8.1% and 10.5% for young recipients treated with thymoglobulin and basiliximab (P > .05), respectively]. Older recipients treated with thymoglobulin showed the poorest survival in the Cox regression model adjusted for comorbidities. Thus thymoglobulin should be used with caution in older recipients during the present pandemic era.
Keywords: COVID-19 infection; basiliximab; lymphocyte-depleting agents; renal transplantation.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
References
-
- Santeusanio AD, Zendel A, Fenig Yet al. . Kidney transplantation using lymphocyte depleting induction and standard maintenance immunosuppression at the height of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in New York City: a single-center experience. Clin Transplant 2020; 34: e14055. - PubMed

