Emerging nanosensor platforms and machine learning strategies toward rapid, point-of-need small-molecule metabolite detection and monitoring
- PMID: 36320477
- PMCID: PMC9516957
- DOI: 10.1039/d2sc02981b
Emerging nanosensor platforms and machine learning strategies toward rapid, point-of-need small-molecule metabolite detection and monitoring
Abstract
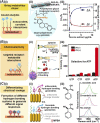
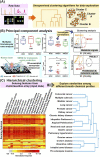
Speedy, point-of-need detection and monitoring of small-molecule metabolites are vital across diverse applications ranging from biomedicine to agri-food and environmental surveillance. Nanomaterial-based sensor (nanosensor) platforms are rapidly emerging as excellent candidates for versatile and ultrasensitive detection owing to their highly configurable optical, electrical and electrochemical properties, fast readout, as well as portability and ease of use. To translate nanosensor technologies for real-world applications, key challenges to overcome include ultralow analyte concentration down to ppb or nM levels, complex sample matrices with numerous interfering species, difficulty in differentiating isomers and structural analogues, as well as complex, multidimensional datasets of high sample variability. In this Perspective, we focus on contemporary and emerging strategies to address the aforementioned challenges and enhance nanosensor detection performance in terms of sensitivity, selectivity and multiplexing capability. We outline 3 main concepts: (1) customization of designer nanosensor platform configurations via chemical- and physical-based modification strategies, (2) development of hybrid techniques including multimodal and hyphenated techniques, and (3) synergistic use of machine learning such as clustering, classification and regression algorithms for data exploration and predictions. These concepts can be further integrated as multifaceted strategies to further boost nanosensor performances. Finally, we present a critical outlook that explores future opportunities toward the design of next-generation nanosensor platforms for rapid, point-of-need detection of various small-molecule metabolites.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Lamichhane S., Sen P., Dickens A. M., Hyötyläinen T. and Orešič M., in Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, ed. J. Jaumot, C. Bedia and R. Tauler, Elsevier, 2018, vol. 82, pp. 387–413
-
- Ramirez T. Daneshian M. Kamp H. Bois F. Y. Clench M. R. Coen M. Donley B. Fischer S. M. Ekman D. R. Fabian E. Guillou C. Heuer J. Hogberg H. T. Jungnickel H. Keun H. C. Krennrich G. Krupp E. Luch A. Noor F. Peter E. Riefke B. Seymour M. Skinner N. Smirnova L. Verheij E. Wagner S. Hartung T. van Ravenzwaay B. Leist M. ALTEX. 2013;30:209–225. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

