Synthesis, structure and reactivity of μ3-SnH capped trinuclear nickel cluster
- PMID: 36320577
- PMCID: PMC9533397
- DOI: 10.1039/d2sc04042e
Synthesis, structure and reactivity of μ3-SnH capped trinuclear nickel cluster
Abstract
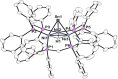
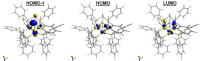
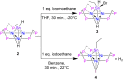
Treatment of the trichlorotin-capped trinuclear nickel cluster, [Ni3(dppm)3(μ3-Cl)(μ3-SnCl3)], 1, with 4 eq. NaHB(Et)3 yields a μ3-SnH capped trinuclear nickel cluster, [Ni3(dppm)3(μ3-H)(μ3-SnH)], 2 [dppm = bis(diphenylphosphino)methane]. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and computational studies together support that cluster 2 is a divalent tin hydride. Complex 2 displays a wide range of reactivity including oxidative addition of bromoethane across the Sn center. Addition of 1 eq. iodoethane to complex 2 releases H2 (g) and generates an ethyltin-capped nickel cluster with a μ3-iodide, [Ni3(dppm)3(μ3-I)(μ3-Sn(CH2CH3))], 4. Notably, insertion of alkynes into the Sn-H bond of 2 can be achieved via addition of 1 eq. 1-hexyne to generate the 1-hexen-2-yl-tin-capped nickel cluster, [Ni3(dppm)3(μ3H)(μ3-Sn(C6H11))], 5. Addition of H2 (g) to 5 regenerates the starting material, 2, and hexane. The formally 44-electron cluster 2 also displays significant redox chemistry with two reversible one-electron oxidations (E = -1.3 V, -0.8 V vs. Fc0/+) and one-electron reduction process (E = -2.7 V vs. Fc0/+) observed by cyclic voltammetry.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
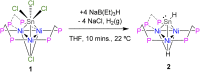

References
-
- Davies A. G., Organotin chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 2006
-
- Pereyre M., Quintard J.-P. and Rahm A., Tin in organic synthesis, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2013
-
- Rivard E. Fischer R. C. Wolf R. Peng Y. Merrill W. A. Schley N. D. Zhu Z. Pu L. Fettinger J. C. Teat S. J. Nowik I. Herber R. H. Takagi N. Nagase S. Power P. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:16197–16208. - PubMed
-
- Eichler B. E. Power P. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:8785–8786.
-
- Peng Y. Ellis B. D. Wang X. Power P. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:12268–12269. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

