Evaluation of right ventricular performance in patients with postoperative congenital heart disease using Doppler tissue imaging and cardiopulmonary bypass indices: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 36320652
- PMCID: PMC9617649
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.909
Evaluation of right ventricular performance in patients with postoperative congenital heart disease using Doppler tissue imaging and cardiopulmonary bypass indices: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background and aims: Postoperative cardiac outcomes after intracardiac repair (ICR) are determined by numerous factors whereas right ventricle (RV) dysfunction is considered essential for them, as only few studies attempted to evaluate it postsurgically. RV's function is supposed to be the strong prognostic factor for patients diagnosed with congenital heart defects; therefore, assessing it is the main objective of the study.
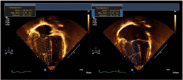
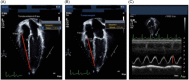
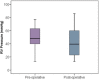
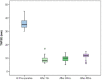
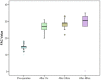
Methods: This is a prospective single-centered cohort study performed on 50 pediatric patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) who underwent ICR between January 2019 and January 2022. All patients underwent echocardiographic assessment of RV function via tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and fractional area change (FAC) at 1, 24, and 48 h. After surgery, where pre- and postoperative RV pressure, cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), and aortic cross-clamp (ACC) time were assessed. Similarly ventilation intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital stay times and mediastinal drainage were also monitored.
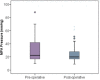
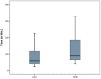
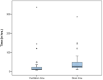
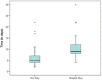
Results: The mean ± standard deviation for pre- and postoperative RV pressure was 49.1 ± 16.12 and 42.7 ± 2.9 mmHg, respectively, whereas that for pre- and postoperative pulmonary artery pressure was 30.4 ± 2.6 and 24.2 ± 12.9 mmHg, with p value of <0.002 and <0.001, respectively. The mean ± standard deviation of CPB and ACC times was 120.92 ± 74.17 and 78.44 ± 50.5 min accordingly, while those for mean ± standard deviation of ventilation time, mediastinum chest drainage, ICU and hospital stays were 30.36 ± 54.04, 43.78 ± 46.7 min, 5.9 ± 4.01 h, were 30.36 ± 54.0, 43.78 ± 46.7 min, 5.9 ± 4.01 and 10.3 ± 4.83 h, respectively.
Conclusions: RV dysfunction plays the important role in longer recovery and intraoperative time, while its effect is mostly transient. The use of TAPSE and FAC methods is valuable in the evaluation of postoperative outcomes, and the former proved to be more effective.
Keywords: Doppler tissue imaging; cardiopulmonary bypass; congenital heart disease; intracardiac repair; ventricular performance.
© 2022 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

