A cross-sectional study of the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the physical activity of Jordanian population
- PMID: 36320655
- PMCID: PMC9616167
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.896
A cross-sectional study of the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the physical activity of Jordanian population
Abstract
Background: Since the declaration of the COVID-19 pandemic on 11th March 2020, the public health recommendations have applied lockdowns and restrictions to limit the spread of the disease. These measures determined outdoor activities and access to many forms of exercise.
Objective: The primary objective of this study was to examine the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the physical activity (PA) of the Jordanian population.
Methods: A cross-sectional online survey was designed using Google Forms services and distributed on social media platforms during the first two weeks of November 2020 to evaluate the exercise activity changes during the COVID-19 pandemic in the study population. In this research, we included those who perform any form of physical activity (n = 1103). The data collected were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 26 (IBM SPSS Corp, SPSS Statistics ver. 26, USA). The categorical variables were summarized as frequencies and proportions and were compared using the Chi-square. For all analyses, P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
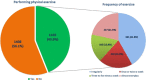
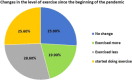
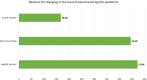
Results: A total of 1103 out of 2,511 (43.9%) respondents who participated in the survey were physically exercising during the COVID-19 pandemic. 41.8% were exercising at an irregular frequency, while 21.5% were exercising daily, 16.8% were exercising three to five times a week, and 19.9% were exercising once or twice a week. Moreover, 282 (25.6%) respondents started doing some form of exercise during the pandemic. Those significantly were less than 18-year-old, male gender, were single, were non-smokers, and had a diploma or bachelor's degree in a health-related major. These changes in the level of exercise have been attributed by 57.8% of respondents to the health aspects where they realized the importance of exercising in strengthening the immune system against diseases, including COVID-19.
Conclusion: The current study showed that lockdown, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, had a positive impact on the healthy lifestyle of the Jordanian population which was attributed to their feeling of the importance of sports practice on the immune system and the availability of time for those activities. However, the younger and individuals were more aware of the importance of these practices which highlights the importance of considering other age groups in future studies of healthy behaviors.
Keywords: COVID‐19; exercise; health; lifestyle; lockdown; physical activity.
© 2022 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown on smoking habits and lifestyle: A cross-sectional study.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 30;6(7):e1392. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1392. eCollection 2023 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37396557 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise behavior, practice, injury, and symptoms of respiratory tract infection of 502 Brazilian adults during lockdown oscillations in two years (2021-2022) of the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023 Aug 1;15(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13102-023-00701-8. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37528434 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of COVID-19 on Physical Activity Among Adults in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2022 Jul 5;14(7):e26586. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26586. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35936172 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on lifestyle among the Saudi population.J Public Health Res. 2022 Sep 10;11(3):22799036221123156. doi: 10.1177/22799036221123156. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Public Health Res. 2022. PMID: 36105779 Free PMC article.
-
JCOA The Japanese Clinical Orthopaedic Association the questionnaire survey on the physical changes after the self-restraint of outdoor activities with the COVID-19 crisis (2nd report).J Orthop Sci. 2024 Jan;29(1):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2023.08.023. Epub 2023 Nov 6. J Orthop Sci. 2024. PMID: 37940467 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown on smoking habits and lifestyle: A cross-sectional study.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 30;6(7):e1392. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1392. eCollection 2023 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37396557 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and Reliability of a Questionnaire Assessing Changes in Dietary Behaviors Among School Children Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic in Jordan.Cureus. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):e66980. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66980. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Physical Activity. World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Announces COVID‐19 Outbreak a Pandemic. World Health Organization; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

