Mechanism of calcium in melatonin enhancement of functional substance-phenolic acid in germinated hulless barley
- PMID: 36320768
- PMCID: PMC9557744
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra05289j
Mechanism of calcium in melatonin enhancement of functional substance-phenolic acid in germinated hulless barley
Abstract
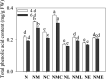
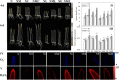
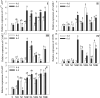
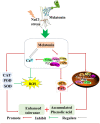
Phenolic acid is a physiologically active substance that has a variety of effects on humans. Barley sprouts are often used as food ingredients to enrich phenolic acids and to further produce functional foods rich in phenolic acids. In this study, the mechanism of Ca2+ involvement in regulating phenolic acid biosynthesis and plant growth in barley by melatonin (MT) under NaCl stress was investigated. According to the studies, MT (25 μM) increased total calcium content, induced Ca2+ burst, and up-regulated the gene expression of calcium-regulated protein-dependent protein kinase and calcium-binding protein transcription-activating protease in NaCl-stressed (60 mM) barley. Exogenous MT and its combined CaCl2 (0.4 mM) significantly promoted phenolic acid biosynthesis by increasing the activity of C4H and PAL, and induced gene expression of PAL and F5H. The addition of exogenous CaCl2 and MT caused systemic tolerance in NaCl-stressed barley, as determined by a decrease in the fluorescence intensity of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen radical anions as well as an enhancement in the antioxidant enzyme, thus significantly increasing sprout length and fresh weight. In addition, combined use of MT with Ca2+ antagonists (lanthanum chloride or ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid), impaired all impacts as mentioned above. These findings imply that Ca2+ participated in MT-induced phenolic acid biosynthesis and growth improvement in NaCl-stressed barley.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of exogenous melatonin involved in phenolic acid metabolism of germinated hulless barley under NaCl stress.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Jan 1;170:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.11.036. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34844114
-
Role of Ca2+ in phenolic compound metabolism of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) sprouts under NaCl stress.J Sci Food Agric. 2019 Aug 30;99(11):5176-5186. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9764. Epub 2019 May 24. J Sci Food Agric. 2019. PMID: 31021402
-
Melatonin mediates phenolic acids accumulation in barley sprouts under MeJA stress.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 4;11:1403293. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1403293. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38899320 Free PMC article.
-
Function, Mechanism, and Application of Plant Melatonin: An Update with a Focus on the Cereal Crop, Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;11(4):634. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040634. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total polyphenols and bioactivity of seeds and sprouts in several legumes.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(34):6112-24. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319340005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448441 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of ROS and calcium ions in developing heat resistance and inducing antioxidant system of wheat seedlings under melatonin's effects.Protoplasma. 2024 Sep;261(5):975-989. doi: 10.1007/s00709-024-01952-z. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Protoplasma. 2024. PMID: 38622466
-
Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal the role of calcium sugar alcohol in the regulation of phenolic acid biosynthesis in Torreya grandis nuts.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 23;25(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06113-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39844048 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin-Mediated Molecular Responses in Plants: Enhancing Stress Tolerance and Mitigating Environmental Challenges in Cereal Crop Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 21;25(8):4551. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084551. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methyl Jasmonate and Zinc Sulfate Induce Secondary Metabolism and Phenolic Acid Biosynthesis in Barley Seedlings.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 30;13(11):1512. doi: 10.3390/plants13111512. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891320 Free PMC article.
-
Phytomelatonin: A key regulator of redox and phytohormones signaling against biotic/abiotic stresses.Redox Biol. 2023 Aug;64:102805. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102805. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37406579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bento-Silva A. Koistinen V. M. Mena P. Bronze M. R. Hanhineva K. Sahlstrm S. Kitryt V. Moco S. Aura A. M. Factors affecting intake, metabolism and health benefits of phenolic acids: do we understand individual variability? Eur. J. Nutr. 2020;9:1275–1293. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-01987-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

