Managing Complexity: The Experience of an Italian Internal Medicine Unit During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic, Looking to the Future
- PMID: 36320815
- PMCID: PMC9610320
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-022-01320-z
Managing Complexity: The Experience of an Italian Internal Medicine Unit During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic, Looking to the Future
Abstract
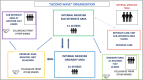
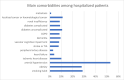
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic put the Italian health system into a test. In the period between September 2020 and June 2021, a weekly average of 114 SARS-CoV-2 infections were recorded in Forlì-Cesena province (north of Italy), with a maximum of 330 cases per week in March 2021; in the same months, the Internal Medicine Unit of Cesena M. Bufalini Hospital managed 954 COVID-19 patients. To allow the management of these patients, the ward was divided into areas at different intensity of care, with a maximum of 39-47 beds and 19-24 in ordinary and sub-intensive area, respectively. Patients had an average age of 66 years, and 62% of the total was female; prevalent comorbidities were arterial hypertension (53%), smoking habit (28.7%), obesity (27.9%), uncomplicated (10%), and complicated diabetes (9%). On the total, 339 patients were hospitalized in sub-intensive area, subjected to non-invasive ventilatory support. Hospitalization lasted about 7 days in the ordinary ward and 13 days in the sub-intensive area. One hundred six patients died. In the considered period, the mean percentage of deaths compared to hospitalizations in Italy was equal to 22.21%; in our experience, the overall mortality rate was 11%. Our organizational model, which included different intensity areas in the same ward and various specialist skills, as the ability to manage non-invasive ventilation and bedside ultrasound, allowed flexible management of the "complex" COVID patient. Even the mortality rate may be the result of this model. These features mark what modern Internal Medicine should be like.
Keywords: COVID-19; Complexity; Health organization; Internal Medicine; Pandemic; Sub-intensive.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. Erratum in: Lancet. 2020 Jan 30. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Characteristics of COVID-19 patients dying in Italy. Available from: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/en/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-analysis-of-deaths. Accessed 20 Oct 2021.
-
- FADOI COVID day. Available from: https://www.fadoi.org/press-room/fadoi-covid-day/. Accessed 30 Nov 2020.
-
- Sanità e protezione civile (2020) Available from: https://www.mef.gov.it/covid-19/Sanita-e-Protezione-Civile/. Accessed 29 Sept 2020.
-
- Epicentro, epidemiology for public health, COVID-19. Available from: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/en/.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous