Ultra-efficient catalytic degradation of malachite green dye wastewater by KMnO4-modified biochar (Mn/SRBC)
- PMID: 36320839
- PMCID: PMC9494031
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra04263k
Ultra-efficient catalytic degradation of malachite green dye wastewater by KMnO4-modified biochar (Mn/SRBC)
Abstract
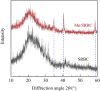
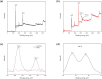
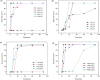
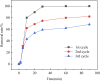
In this work, KMnO4-modified biochar was prepared from spirulina residue as the research object. Herein, we report the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic degradation performance of KMnO4-modified biochar, given that heterogeneous catalytic oxidation is an effective way to treat dye wastewater rapidly. The Mn/SRBC catalyst prepared by KMnO4 modification was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, nitrogen adsorption-desorption and laser Raman spectroscopy. In addition, we compared the results with that of the unmodified SRBC. The results showed that the Mn/SRBC catalyst prepared by KMnO4 modification had a rich pore structure, which provided sufficient contact area for the catalytic reaction. In the presence of H2O2, the catalyst could be used to catalyze the oxidative degradation of malachite green in aqueous solution with ultra-high efficiency. In the experiment, the initial pH values of the reaction system had a significant influence on the reaction rate. The removal effect of biochar on the malachite green was poor in an alkaline environment. Within a specific range, the removal rate of malachite green was proportional to the concentration of H2O2 in the reaction system. The degradation rate of malachite green dye at 8000 mg L-1 was about 99% in the presence of the catalyst over 5 mmol L-1 hydrogen peroxide for 30 min. These results show the potential application of algae residue biochar and carbon-based composite catalysts for degrading and removing dye wastewater.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Swan N. B. Zaini M. A. A. Adsorption of Malachite Green and Congo Red Dyes from Water: Recent Progress and Future Outlook. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S. 2019;26(1):119–132.
-
- Ausavasukhi A. Kampoosaen C. Kengnok O. Adsorption characteristics of Congo red on carbonized leonardite. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016;134:506–514.
-
- Ting A. S. Y. Chin J. E. Biogenic Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles from Apple Peel Extracts for Decolorization of Malachite Green Dye. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2020;231(6):1–10.
-
- Zeng L. Xiao L. Long Y. et al., Trichloroacetic acid-modulated synthesis of polyoxometalate@UiO-66 for selective adsorption of cationic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;516:274–283. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y. Wang G. Wang B. et al., Decolorization of Malachite Green by a Newly Isolated Penicillium sp. YW 01 and Optimization of Decolorization Parameters. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2011;28(8):555–562.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

