An open-source molecular builder and free energy preparation workflow
- PMID: 36320862
- PMCID: PMC9607723
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-022-00754-9
An open-source molecular builder and free energy preparation workflow
Abstract
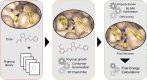
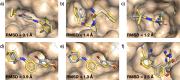
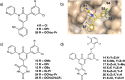
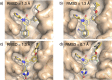
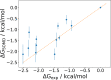
Automated free energy calculations for the prediction of binding free energies of congeneric series of ligands to a protein target are growing in popularity, but building reliable initial binding poses for the ligands is challenging. Here, we introduce the open-source FEgrow workflow for building user-defined congeneric series of ligands in protein binding pockets for input to free energy calculations. For a given ligand core and receptor structure, FEgrow enumerates and optimises the bioactive conformations of the grown functional group(s), making use of hybrid machine learning/molecular mechanics potential energy functions where possible. Low energy structures are optionally scored using the gnina convolutional neural network scoring function, and output for more rigorous protein-ligand binding free energy predictions. We illustrate use of the workflow by building and scoring binding poses for ten congeneric series of ligands bound to targets from a standard, high quality dataset of protein-ligand complexes. Furthermore, we build a set of 13 inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease from the literature, and use free energy calculations to retrospectively compute their relative binding free energies. FEgrow is freely available at https://github.com/cole-group/FEgrow, along with a tutorial.
Keywords: Computational chemistry; Structure-based drug design.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

