A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Scleritis and Pneumonia Initially Diagnosed as Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- PMID: 36320984
- PMCID: PMC9617143
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29725
A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Scleritis and Pneumonia Initially Diagnosed as Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Abstract
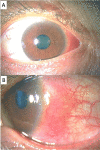
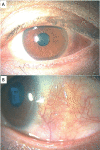
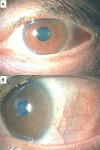
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive plasma cells play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related diseases, in which fibrosis is observed in various organs. Lesions often develop in the lacrimal gland and orbit; however, uveitis and scleritis are also noticed. We present the case of a 55-year-old woman who was diagnosed with eosinophilic pneumonia in November 2021 at the Department of Collagen Disease of another hospital. She was treated with 25 mg of oral prednisolone. On January 11, 2022, when the dose of prednisolone was reduced to 7.5 mg, she began complaining of conjunctival hyperemia in the left eye, and a few days later, eye pain was also reported. On January 17, she visited an ophthalmology clinic and was prescribed betamethasone and tacrolimus eye drops, and was subsequently admitted to our hospital. The blood test results showed a high IgG4 level. We consulted the collagen disease physician to evaluate her previous data. The serum IgG4 level collected on December 6, 2021, was 608 mg/dL, and a re-examination of the bronchial biopsy tissues on December 2, 2021, confirmed 48% of IgG4-positive cells. Thus, pulmonary lesions appeared to be IgG4-related pathologies. Increasing the oral prednisolone dose to 30 mg improved the scleritis. As seen in this case, the possibility of an IgG4-related disease should be considered when scleritis is observed in a patient diagnosed with eosinophilic pneumonia.
Keywords: eosinophil; igg4-related disease; pneumonia; scleritis; steroid.
Copyright © 2022, Fukushima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- IgG4-related disease: review of the histopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic approach. Bledsoe JR, Della-Torre E, Rovati L, Deshpande V. APMIS. 2018;126:459–476. - PubMed
-
- Clinical features and symptoms of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: a multicenter study. Goto H, Ueda SI, Nemoto R, et al. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2021;65:651–656. - PubMed
-
- IgG4-related disease in the eye and ocular adnexa. Derzko-Dzulynsky L. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2017;28:617–622. - PubMed
-
- Role of eosinophilia in IgG4-related disease. Ming B, Zhong J, Dong L. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:1038–1044. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
