Prone Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Protocol: A Single-Center Experience at Implementation and Review of Literature
- PMID: 36321034
- PMCID: PMC9600933
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29604
Prone Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Protocol: A Single-Center Experience at Implementation and Review of Literature
Abstract
The prone position is a crucial position used in the operating rooms and the intensive care units, with its importance highly recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a cardinal procedure that is indicated and performed on any eligible patient who has cardiopulmonary arrest and resultant lack of perfusion and oxygenation. When a patient has a cardiopulmonary arrest in the prone position, the options include rotating the patient supine before starting cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or beginning CPR while prone. Prone CPR has not had a widely accepted use so far. In this article, we narrate the process of protocol development and staff education at our hospital for the initiation of prone CPR and review the literature related to it. Prone CPR is an effective technique with good outcomes and involves a learning curve. Appropriate training needs to be done before implementing the protocol, and adequate quality control measures need to be set to ensure that the skill set is maintained.
Keywords: cardiac arrest; cardiac resuscitation; cardiopulmonary resuscitation; in hospital cardiac arrest; prone cpr; prone position; quality improvement and patient safety; resuscitation education.
Copyright © 2022, McCraw et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
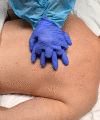
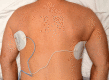
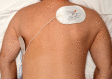
References
-
- Prone positioning for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Hadaya J, Benharash P. JAMA. 2020;324:1361. - PubMed
-
- Interim guidance for basic and advanced life support in adults, children, and neonates with suspected or confirmed COVID- 19: from the emergency cardiovascular care committee and get with the guidelines-resuscitation adult and pediatric task forces of the American Heart Association. Edelson DP, Sasson C, Chan PS, et al. Circulation. 2020;141:0–43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice: Appendix D. [ Sep; 2022 ]. 2017. https://www.mghpcs.org/eed/ebp/Assets/documents/pdf/2017_Appendix%20D_Ev... https://www.mghpcs.org/eed/ebp/Assets/documents/pdf/2017_Appendix%20D_Ev...
-
- Optimizing prone cardiopulmonary resuscitation: identifying the vertebral level correlating with the largest left ventricle cross-sectional area via computed tomography scan. Kwon MJ, Kim EH, Song IK, Lee JH, Kim HS, Kim JT. Anesth Analg. 2017;124:520–523. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
