Dasatinib/prednisone induction followed by blinatumomab/dasatinib in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 36322825
- PMCID: PMC10090098
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008216
Dasatinib/prednisone induction followed by blinatumomab/dasatinib in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
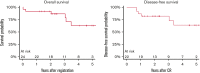
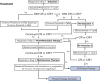
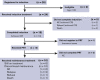
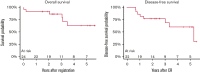
Novel treatment strategies are needed for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in older patients. This trial evaluated the feasibility and outcomes with the anti-CD19 bispecific T-cell-engaging antibody, blinatumomab, in combination with dasatinib and steroids. Patients 65 years of age or older with Ph+ or Ph-like ALL (with dasatinib-sensitive fusions/mutations) were eligible and could be newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory. Induction therapy consisted of dasatinib/prednisone. Patients not achieving response by day 56 proceeded to blinatumomab reinduction therapy. Patients achieving response with induction or reinduction therapy proceeded to blinatumomab/dasatinib postremission therapy for 3 cycles followed by dasatinib/prednisone maintenance. All patients received central nervous system prophylaxis with intrathecal methotrexate for a total of 8 doses. Response was assessed at days 28, 56, and 84 and at additional time points based on response parameters. Measurable residual disease was assessed centrally by 8-color flow cytometry at day 28. A total of 24 eligible patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL were enrolled with a median age of 73 years (range, 65-87 years). This combination was safe and feasible. With a median of 2.7 years of follow-up, 3-year overall survival and disease-free survival were 87% (95% confidence interval [CI], 64-96) and 77% (95% CI, 54-90), respectively. Although longer follow-up is needed, these results are encouraging, and future trials are building on this backbone regimen. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02143414.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.S.A. is a member on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees for Kite Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmacueticals, Glycomimetics, Seattle Genetics, and Amgen; receives research funding from Kite Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Glycomimetics, Immunogen, OBI, Seattle Genetics, Servier, Incyte, Pfizer, Macrogenics, and Amgen; and receives honoraria from Pfizer. A.M. provided consultancy for BioSight Ltd. B.L.W. reports laboratory service agreements for testing to support clinical trials for Novartis, Kite, Macrogenics, and Wugen; and a consultancy agreement with Kite. J.P. provided consultancy for Intellia, Kura Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb, Affyimmune, Curocel, Novartis, Artiva, PrecisionBio, Servier, Kite Pharma, Innate Pharma, Minerva, Autolus, and Amgen. M.W. is a current member on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees for Gilead and a current holder of stock options in a privately held company, Reata. D.J. receives research funding from Jazz and Pfizer
Myers Squibb, Celgene - a Bristol Myers Squibb company, Incyte Corporation, Jazz Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Novartis; serves on an independent review committee for AbbVie Inc. and on an advisory committee for Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc., Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene - a Bristol Myers Squibb company, Daiichi Sankyo Inc., Genentech - a member of the Roche Group, GlycoMimetics Inc., Incyte Corporation, Jazz Pharmaceuticals Inc., Kura Oncology, and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for B.L.W. is Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA.
The current affiliation for M.W. is University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, OK.
Figures
References
-
- Foa R, Vignetti M, Meloni G, et al. Dasatinib as first-line treatment for adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118(25):6521–6528. - PubMed