Discovery and structural characterization of chicoric acid as a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein ligand and RNA binding disruptor
- PMID: 36323732
- PMCID: PMC9628480
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22576-4
Discovery and structural characterization of chicoric acid as a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein ligand and RNA binding disruptor
Abstract
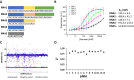
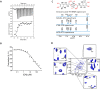
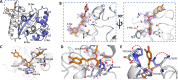
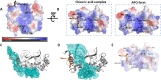
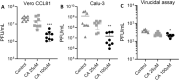
The nucleocapsid (N) protein plays critical roles in coronavirus genome transcription and packaging, representing a key target for the development of novel antivirals, and for which structural information on ligand binding is scarce. We used a novel fluorescence polarization assay to identify small molecules that disrupt the binding of the N protein to a target RNA derived from the SARS-CoV-2 genome packaging signal. Several phenolic compounds, including L-chicoric acid (CA), were identified as high-affinity N-protein ligands. The binding of CA to the N protein was confirmed by isothermal titration calorimetry, 1H-STD and 15N-HSQC NMR, and by the crystal structure of CA bound to the N protein C-terminal domain (CTD), further revealing a new modulatory site in the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Moreover, CA reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in cell cultures. These data thus open venues for the development of new antivirals targeting the N protein, an essential and yet underexplored coronavirus target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural insights into the RNA binding inhibitors of the C-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid.J Struct Biol. 2025 Jun;217(2):108197. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2025.108197. Epub 2025 Mar 18. J Struct Biol. 2025. PMID: 40113149
-
Mechanistic and thermodynamic characterization of antiviral inhibitors targeting nucleocapsid N-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023 Dec;750:109820. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109820. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37956938
-
Unveiling potential inhibitors targeting the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2: Structural insights into their binding sites.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jul;273(Pt 2):133167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133167. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38885868
-
Corona virus versus existence of human on the earth: A computational and biophysical approach.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Oct 15;161:271-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.007. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32512089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2.Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3-11. Malays J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32342926 Review.
Cited by
-
Serodominant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Peptides Map to Unstructured Protein Regions.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0032423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00324-23. Epub 2023 May 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37191546 Free PMC article.
-
ECHOPvir: A Mixture of Echinacea and Hop Extracts Endowed with Cytoprotective, Immunomodulatory and Antiviral Properties.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 16;15(20):4380. doi: 10.3390/nu15204380. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37892456 Free PMC article.
-
ISGylation of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein by HERC5 impedes N oligomerization and thereby viral RNA synthesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 20:2024.05.15.594393. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.15.594393. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Virol. 2024 Sep 17;98(9):e0086924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00869-24. PMID: 39149229 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Natural product sennoside B disrupts liquid-liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein by inhibiting its RNA-binding activity.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025 Dec;40(1):2501743. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2501743. Epub 2025 May 15. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40371698 Free PMC article.
-
Generative adversarial network (GAN) model-based design of potent SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors using the electron density of ligands and 3D binding pockets: insights from molecular docking, dynamics simulation, and MM-GBSA analysis.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3059-3075. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11047-9. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39613993
References
-
- Das, S., Wingender, P., Barrett, P., Pugacheva, E. & Magistretti, G. After-effects of the COVID-19 pandemic: Prospects for medium-term economic damage. In IMF Working Papers2021, 1 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

