Discovery and structural characterization of chicoric acid as a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein ligand and RNA binding disruptor
- PMID: 36323732
- PMCID: PMC9628480
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22576-4
Discovery and structural characterization of chicoric acid as a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein ligand and RNA binding disruptor
Abstract
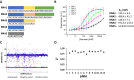
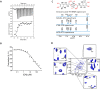
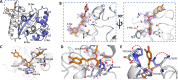
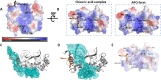
The nucleocapsid (N) protein plays critical roles in coronavirus genome transcription and packaging, representing a key target for the development of novel antivirals, and for which structural information on ligand binding is scarce. We used a novel fluorescence polarization assay to identify small molecules that disrupt the binding of the N protein to a target RNA derived from the SARS-CoV-2 genome packaging signal. Several phenolic compounds, including L-chicoric acid (CA), were identified as high-affinity N-protein ligands. The binding of CA to the N protein was confirmed by isothermal titration calorimetry, 1H-STD and 15N-HSQC NMR, and by the crystal structure of CA bound to the N protein C-terminal domain (CTD), further revealing a new modulatory site in the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Moreover, CA reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in cell cultures. These data thus open venues for the development of new antivirals targeting the N protein, an essential and yet underexplored coronavirus target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Das, S., Wingender, P., Barrett, P., Pugacheva, E. & Magistretti, G. After-effects of the COVID-19 pandemic: Prospects for medium-term economic damage. In IMF Working Papers2021, 1 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

