Inulin fibre promotes microbiota-derived bile acids and type 2 inflammation
- PMID: 36323778
- PMCID: PMC10576985
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05380-y
Inulin fibre promotes microbiota-derived bile acids and type 2 inflammation
Abstract
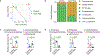
Dietary fibres can exert beneficial anti-inflammatory effects through microbially fermented short-chain fatty acid metabolites<sup>1,2</sup>, although the immunoregulatory roles of most fibre diets and their microbiota-derived metabolites remain poorly defined. Here, using microbial sequencing and untargeted metabolomics, we show that a diet of inulin fibre alters the composition of the mouse microbiota and the levels of microbiota-derived metabolites, notably bile acids. This metabolomic shift is associated with type 2 inflammation in the intestine and lungs, characterized by IL-33 production, activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells and eosinophilia. Delivery of cholic acid mimics inulin-induced type 2 inflammation, whereas deletion of the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor diminishes the effects of inulin. The effects of inulin are microbiota dependent and were reproduced in mice colonized with human-derived microbiota. Furthermore, genetic deletion of a bile-acid-metabolizing enzyme in one bacterial species abolishes the ability of inulin to trigger type 2 inflammation. Finally, we demonstrate that inulin enhances allergen- and helminth-induced type 2 inflammation. Taken together, these data reveal that dietary inulin fibre triggers microbiota-derived cholic acid and type 2 inflammation at barrier surfaces with implications for understanding the pathophysiology of allergic inflammation, tissue protection and host defence.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



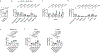



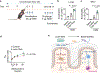




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI140724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR070116/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095466/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 HD101401/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 DK132244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126871/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI151599/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI172027/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002385/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM131877/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL134629/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

