Descending projections to the auditory midbrain: evolutionary considerations
- PMID: 36323876
- PMCID: PMC9898193
- DOI: 10.1007/s00359-022-01588-5
Descending projections to the auditory midbrain: evolutionary considerations
Abstract
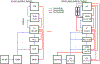
The mammalian inferior colliculus (IC) is massively innervated by multiple descending projection systems. In addition to a large projection from the auditory cortex (AC) primarily targeting the non-lemniscal portions of the IC, there are less well-characterized projections from non-auditory regions of the cortex, amygdala, posterior thalamus and the brachium of the IC. By comparison, the frog auditory midbrain, known as the torus semicircularis, is a large auditory integration center that also receives descending input, but primarily from the posterior thalamus and without a projection from a putative cortical homolog: the dorsal pallium. Although descending projections have been implicated in many types of behaviors, a unified understanding of their function has not yet emerged. Here, we take a comparative approach to understanding the various top-down modulators of the IC to gain insights into their functions. One key question that we identify is whether thalamotectal projections in mammals and amphibians are homologous and whether they interact with evolutionarily more newly derived projections from the cerebral cortex. We also consider the behavioral significance of these descending pathways, given anurans' ability to navigate complex acoustic landscapes without the benefit of a corticocollicular projection. Finally, we suggest experimental approaches to answer these questions.
Keywords: Anuran; Auditory cortex; Bat; Corticofugal; Echolocation; Frog; Inferior colliculus; Thalamus.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Figures


References
-
- Adams JC (1980) Crossed and descending projections to the inferior colliculus. Neurosci Lett 19 (1):1–5 - PubMed
-
- Aitkin LM, Phillips SC (1984) Is the inferior colliculus and obligatory relay in the cat auditory system? Neurosci Lett 44 (3):259–264 - PubMed
-
- Arak A (1983) Sexual selection by male–male competition in natterjack toad choruses. Nature 306 (5940):261–262
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

