Prognostic nutritional index as a risk factor for diabetic kidney disease and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 36324018
- PMCID: PMC9629877
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-022-01985-x
Prognostic nutritional index as a risk factor for diabetic kidney disease and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aims: Microinflammation and malnutrition are common in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to validate whether prognostic nutritional index (PNI) may increase the risk of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and all-cause mortality in T2DM patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and National Death Index (NDI) 2013-2018 database. A total of 14,349 eligible subjects were included, and 2720 of them were with T2DM. PNI was assessed by the 5 × lymphocyte count (109/L) + serum albumin (g/L). The Logistic and Cox regression analyses were conducted to investigate the risk factors of DKD and mortality in T2DM patients.
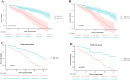
Results: For 14,349 participants represented 224.7 million noninstitutionalized residents of the United State, the average PNI was 53.72 ± 0.12, and the prevalence of T2DM was 14.89%. T2DM patients had a lower level of PNI and dietary protein intake, a higher risk of mortality, kidney injury, anemia, arterial hypertension and hyperuricemia, compared with non-T2DM subjects. DKD occurred in 35.06% of diabetic participants and a higher PNI was independently related with a lower risk of DKD (OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.459-0.892, p = 0.01) in T2DM after multivariate adjustment. During a median follow-up of 46 person-months (29-66 months), a total of 233 T2DM individuals died from all causes (mortality rate = 8.17%). Subjects with T2DM who had a higher PNI showed a lower risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.60, 95% CI 0.37-0.97, p = 0.036).
Conclusions: PNI, as a marker of immunonutrition, correlated with the incidence of DKD, and was an independent predictor for all-cause mortality in participants with T2DM. Thus, PNI may conduce to the risk stratification and timely intervention of T2DM patients.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Diabetic kidney disease; Immunonutrition; Prognostic nutritional index; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. Springer-Verlag Italia S.r.l., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Diabetes around the world in 2021. The IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition [Internet] ed: International Diabetes Federation. p. Available from https://diabetesatlas.org/.
-
- Shaman AM, Bain SC, Bakris GL, et al. Effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists semaglutide and liraglutide on kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a pooled analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER trials. Circulation. 2021;145:575–585. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055459. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO’s Global Health Estimates (GHE) [Internet]. pp. Available from https://www.who.int/data/global-health-estimates/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

