Common Gray Matter Reductions in Alcohol Use and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 36324652
- PMCID: PMC9616258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.11.010
Common Gray Matter Reductions in Alcohol Use and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Though compulsive drinking is a hallmark of alcohol use disorder (AUD), little is known of the neural mechanisms driving this behavior. To further the understanding of the neural underpinnings of this compulsivity, a meta-analytic approach was used to examine gray matter (GM) volume differences related to AUD, and contrast these differences with GM volume differences in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), to find common underlying regional brain differences.
Methods: We systematically meta-analyzed case-control studies investigating GM volume that used whole-brain voxel-based morphometry separately for AUD and OCD and then directly compared the results of both. Seed-based d Mapping software was used to perform the meta-analyses.
Results: The AUD meta-analysis used 19 citations, with 736 individuals with AUD and 827 control individuals. The OCD meta-analysis had 25 citations, with 995 individuals with OCD and 1177 control individuals. The AUD group showed decreased GM in areas including frontal, limbic, temporal, and cerebellar regions. The OCD group had decreased GM in frontal and insular regions but increases in the hypothalamus and brainstem. Importantly, the main outcome showed that both groups had decreased GM overlapping in the anterior cingulate cortex and insula. Brain regions were p < .05 corrected.
Conclusions: Common brain regional differences in the anterior cingulate cortex and insula that overlap between AUD and OCD suggest that interventions targeting these regions could prove to be beneficial in treating compulsive drinking related to AUD. Further research into the functional role of these brain regions in the etiology of compulsive drinking in AUD is warranted.
Keywords: ACC; AUD; Compulsivity; Meta-analysis; OCD; VBM.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Inc on behalf of Society of Biological Psychiatry.
Figures
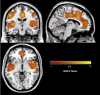
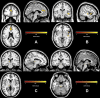
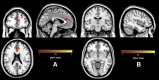
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta: 2013. Alcohol and Public Health: Alcohol-Related Disease Impact (ARDI): Average for United States 2006-2010: Alcohol-Attributable Deaths Due to Excessive Alcohol Use.
-
- Hasin D.S., Stinson F.S., Ogburn E., Grant B.F. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:830–842. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

