Microneedle-mediated drug delivery for cutaneous diseases
- PMID: 36324904
- PMCID: PMC9618658
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1032041
Microneedle-mediated drug delivery for cutaneous diseases
Abstract
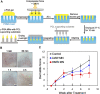
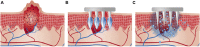
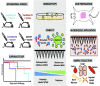
Microneedles have garnered significant interest as transdermal drug delivery route owing to the advantages of nonselective loading capacity, minimal invasiveness, simple operation, and good biocompatibility. A number of therapeutics can be loaded into microneedles, including hydrophilic and hydrophobic small molecular drugs, and macromolecular drugs (proteins, mRNA, peptides, vaccines) for treatment of miscellaneous diseases. Microneedles feature with special benefits for cutaneous diseases owing to the direct transdermal delivery of therapeutics to the skin. This review mainly introduces microneedles fabricated with different technologies and transdermal delivery of various therapeutics for cutaneous diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, skin and soft tissue infection, superficial tumors, axillary hyperhidrosis, and plantar warts.
Keywords: cutaneous disease; drug delivery; microneedle; microneedle fabrication; transdermal route.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Ren, Zhou, Zheng, Du, Liu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advances in microneedle-based transdermal delivery for drugs and peptides.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Jul;12(7):1556-1568. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01056-8. Epub 2021 Sep 26. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34564827 Review.
-
Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: current trends and fabrication.J Pharm Investig. 2021;51(5):503-517. doi: 10.1007/s40005-021-00512-4. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Pharm Investig. 2021. PMID: 33686358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle Array: Applications, Recent Advances, and Clinical Pertinence in Transdermal Drug Delivery.J Pharm Innov. 2021;16(3):558-565. doi: 10.1007/s12247-020-09460-2. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Pharm Innov. 2021. PMID: 32837607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Microneedle Platforms for Transdermal Drug Delivery Technologies.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;13(15):2405. doi: 10.3390/polym13152405. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34372008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current advances in the fabrication of microneedles for transdermal delivery.J Control Release. 2014 Jul 10;185:130-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.04.052. Epub 2014 May 5. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24806483 Review.
Cited by
-
Microneedle-Assisted Delivery of Curcumin: Evaluating the Effects of Needle Length and Formulation.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;16(2):155. doi: 10.3390/mi16020155. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40047600 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence: A Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 9;15(1):88. doi: 10.3390/biom15010088. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Assembly of Microstructured Protein Coatings with Programmable Functionality for Fluorescent Biosensors.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Nov 20;16(46):63284-63294. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c14249. Epub 2024 Nov 6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39501757
-
Microneedling in Dermatology: A Comprehensive Review of Applications, Techniques, and Outcomes.Cureus. 2024 Sep 23;16(9):e70033. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70033. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39449889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle delivery system with rapid dissolution and sustained release of bleomycin for the treatment of hemangiomas.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 25;22(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02557-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38918811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Qallaf B., Das D. B. (2008). Optimization of square microneedle arrays for increasing drug permeability in skin. Chem. Eng. Sci. 63 (9), 2523–2535. 10.1016/j.ces.2008.02.007 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

