Strategy to avoid vascular injuries in revision total hip arthroplasty with intrapelvic implants
- PMID: 36325631
- PMCID: PMC9709496
- DOI: 10.1302/2633-1462.311.BJO-2021-0188.R1
Strategy to avoid vascular injuries in revision total hip arthroplasty with intrapelvic implants
Abstract
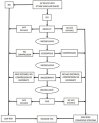
Aims: Our objective was describing an algorithm to identify and prevent vascular injury in patients with intrapelvic components.
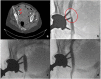
Methods: Patients were defined as at risk to vascular injuries when components or cement migrated 5 mm or more beyond the ilioischial line in any of the pelvic incidences (anteroposterior and Judet view). In those patients, a serial investigation was initiated by a CT angiography, followed by a vascular surgeon evaluation. The investigation proceeded if necessary. The main goal was to assure a safe tissue plane between the hardware and the vessels.
Results: In ten at-risk patients undergoing revision hip arthroplasty and submitted to our algorithm, six were recognized as being high risk to vascular injury during surgery. In those six high-risk patients, a preventive preoperative stent was implanted before the orthopaedic procedure. Four patients needed a second reinforcing stent to protect and to maintain the vessel anatomy deformed by the intrapelvic implants.
Conclusion: The evaluation algorithm was useful to avoid blood vessels injury during revision total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients.Cite this article: Bone Jt Open 2022;3(11):859-866.
Keywords: Hip; Hip arthroplasty; Intrapelvic implants; Vascular System Injuries.
Figures


References
-
- Kawasaki Y, Egawa H, Hamada D, Takao S, Nakano S, Yasui N. Location of intrapelvic vessels around the acetabulum assessed by three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography: prevention of vascular-related complications in total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2012;17(4):397–406. 10.1007/s00776-012-0227-7 - DOI - PubMed

