Increased autophagy leads to decreased apoptosis during β-thalassaemic mouse and patient erythropoiesis
- PMID: 36329049
- PMCID: PMC9633749
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21249-6
Increased autophagy leads to decreased apoptosis during β-thalassaemic mouse and patient erythropoiesis
Abstract
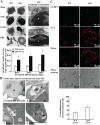
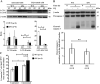
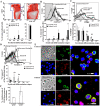
β-Thalassaemia results from defects in β-globin chain production, leading to ineffective erythropoiesis and subsequently to severe anaemia and other complications. Apoptosis and autophagy are the main pathways that regulate the balance between cell survival and cell death in response to diverse cellular stresses. Herein, the death of erythroid lineage cells in the bone marrow from both βIVS2-654-thalassaemic mice and β-thalassaemia/HbE patients was investigated. Phosphatidylserine (PS)-bearing basophilic erythroblasts and polychromatophilic erythroblasts were significantly increased in β-thalassaemia as compared to controls. However, the activation of caspase 8, caspase 9 and caspase 3 was minimal and not different from control in both murine and human thalassaemic erythroblasts. Interestingly, bone marrow erythroblasts from both β-thalassaemic mice and β-thalassaemia/HbE patients had significantly increased autophagy as shown by increased autophagosomes and increased co-localization between LC3 and LAMP-1. Inhibition of autophagy by chloroquine caused significantly increased erythroblast apoptosis. We have demonstrated increased autophagy which led to minimal apoptosis in β-thalassaemic erythroblasts. However, increased PS exposure occurring through other mechanisms in thalassaemic erythroblasts might cause rapid phagocytic removal by macrophages and consequently ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassaemia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Taher AT, Musallam KM, Cappellini MD. β-Thalassemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:727–743. - PubMed
-
- Pootrakul P, et al. A correlation of erythrokinetics, ineffective erythropoiesis, and erythroid precursor apoptosis in thai patients with thalassemia. Blood. 2000;96:2606–2612. - PubMed
-
- Centis F, et al. The importance of erythroid expansion in determining the extent of apoptosis in erythroid precursors in patients with β-thalassemia major. Blood. 2000;96:3624–3629. - PubMed
-
- Mathias LA, et al. Ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia major is due to apoptosis at the polychromatophilic normoblast stage. Exp. Hematol. 2000;28:1343–1353. - PubMed
-
- Yuan J, et al. Accelerated programmed cell death (apoptosis) in erythroid precursors of patients with severe β-thalassemia (Cooley's anemia) Blood. 1993;82:374–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

