Guominkang formula alleviate inflammation in eosinophilic asthma by regulating immune balance of Th1/2 and Treg/Th17 cells
- PMID: 36330091
- PMCID: PMC9624229
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.978421
Guominkang formula alleviate inflammation in eosinophilic asthma by regulating immune balance of Th1/2 and Treg/Th17 cells
Abstract
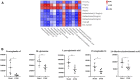
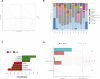
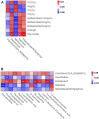
The number of patients with allergic asthma is rising yearly, and hormonal drugs, such as dexamethasone, have unique advantages and certain limitations. In the treatment of allergic diseases especially allergic asthma, increasing the percentage or the function of immunosuppressive cells, such as Treg cells, may achieve a good effect. On the basis of good clinical results, we found that Guominkang (GMK) especially high-concentration GMK can achieve a similar effect with dexamethasone in controlling the symptoms of allergic asthma and inhibiting inflammation of allergic asthma. In our study, GMK can inhibit the recruitment of inflammatory cells, decrease mucus production, and reduce airway resistance. Besides, GMK can reconstruct the cellular immune balance of Th1/2 and Treg/Th17 cells. Metabolome results show that DL-glutamine, L-pyroglutamic acid, prostaglandin b1, prostaglandin e2, and 3,4-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid are the metabolic biomarkers and are associated with Th1/2 and Treg/Th17 cell balance. GMK can also change the gut microbiota in the allergic asthma mouse model. The genus_Muriculum, genus_(Clostridium) GCA900066575, genus_klebsiella, genus_Desulfovibrio, genus_Rikenellaceae RC9 gut group, family_Chitinophagaceae, family_Nocardioidaceae, and genus_Corynebacterium are gut microbiota biomarkers treated by GMK. Among these biomarkers, genus_Muriculum is the gut microbiota biomarker associated with Th1/2 and Treg/Th17 cell balance. Interestingly, we first found that DL-glutamine, L-pyroglutamic acid, prostaglandin b1, prostaglandin e2, and 3,4-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid are all associated with genus_Muriculum. GMK will be a new strategy for the treatment of eosinophilic asthma, and biomarkers will also be a new research direction.
Keywords: GMK; Th1/Th2; Treg/Th17; cellular immune balance; eosinophilic asthma.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Zhao, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
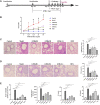
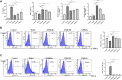
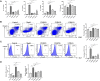
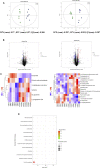
References
-
- Betz M., Fox B. S. (1991). Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J. Immunol. 146, 108–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

