Bergenin inhibits palmitic acid-induced pancreatic β-cell inflammatory death via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 36330410
- PMCID: PMC9622470
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-3781
Bergenin inhibits palmitic acid-induced pancreatic β-cell inflammatory death via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
Background: Bergenin, an active constituent of plants of the genus Bergenia, has been reported to have antidiabetic properties. This study investigated whether bergenin is beneficial for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) via regulating NOD-like receptor family-pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome.
Methods: Two pancreatic β-cell lines, INS-1 and MIN6, were treated with 1, 3, or 10 µM bergenin in the absence or presence of palmitic acid (PA). Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8, flow cytometry, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and immunofluorescent staining were performed.
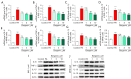
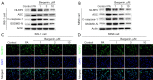
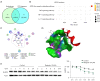
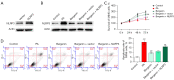
Results: Bergenin with concentrations of 1, 3, and 10 µM had no cytotoxicity in INS-1 and MIN6 cells. However, bergenin dose-dependently relieved PA-induced pancreatic β‑cell loss and apoptosis. Bergenin dose-dependently inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome-related inflammation, as observed by the downregulation of NLRP3, apoptosis associated speck like protein (ASC), cleaved caspase-1, and gasdermin-D (GSDMD)-N, as well as the decreased release of cytokines interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-1β, and IL-18. The NOD-like receptor signaling pathway was predicted to be a downstream signaling pathway regulated by bergenin. Autodock Vina software docked bergenin with NLRP3. The binding energy of interaction was -5.101 kcal/mol and the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) score was 1.5901A. Treating pancreatic β‑cells with bergenin accelerated the degeneration of NLRP3. Furthermore, restoration of NLRP3 expression using plasmid transfection reversed the protective effects of bergenin on pancreatic β-cells.
Conclusions: Our data suggests that bergenin is a potential agent for treating T2DM through preventing NLRP3 inflammasome-related inflammation in pancreatic β-cells.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; NOD-like receptor family-pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3); bergenin; palmitic acid; pancreatic β-cell.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-3781/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
