Early developmental plasticity enables the induction of an intermediate extraembryonic cell state
- PMID: 36332016
- PMCID: PMC9635831
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl9583
Early developmental plasticity enables the induction of an intermediate extraembryonic cell state
Abstract
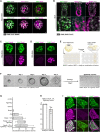
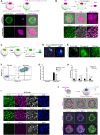
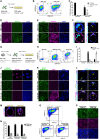
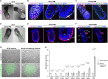
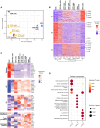
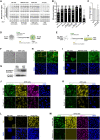
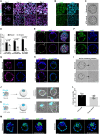
Two fundamental elements of pre-implantation embryogenesis are cells' intrinsic self-organization program and their developmental plasticity, which allows embryos to compensate for alterations in cell position and number; yet, these elements are still poorly understood. To be able to decipher these features, we established culture conditions that enable the two fates of blastocysts' extraembryonic lineages-the primitive endoderm and the trophectoderm-to coexist. This plasticity emerges following the mechanisms of the first lineage segregation in the mouse embryo, and it manifests as an extended potential for extraembryonic chimerism during the pre-implantation embryogenesis. Moreover, this shared state enables robust assembly into higher-order blastocyst-like structures, thus combining both the cell fate plasticity and self-organization features of the early extraembryonic lineages.
Figures

References
-
- Govindasamy N., Duethorn B., Oezgueldez H. O., Kim Y. S., Bedzhov I., Test-tube embryos–Mouse and human development in vitro to blastocyst stage and beyond. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 63, 203–215 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka Y., Lanner F., Rossant J., FGF signal-dependent segregation of primitive endoderm and epiblast in the mouse blastocyst. Development 137, 715–724 (2010). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

