Relay and higher-order thalamic nuclei show an intertwined functional association with cortical-networks
- PMID: 36333448
- PMCID: PMC9636420
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-04126-w
Relay and higher-order thalamic nuclei show an intertwined functional association with cortical-networks
Abstract
Almost all functional processing in the cortex strongly depends on thalamic interactions. However, in terms of functional interactions with the cerebral cortex, the human thalamus nuclei still partly constitute a terra incognita. Hence, for a deeper understanding of thalamic-cortical cooperation, it is essential to know how the different thalamic nuclei are associated with cortical networks. The present work examines network-specific connectivity and task-related topical mapping of cortical areas with the thalamus. The study finds that the relay and higher-order thalamic nuclei show an intertwined functional association with different cortical networks. In addition, the study indicates that relay-specific thalamic nuclei are not only involved with relay-specific behavior but also in higher-order functions. The study enriches our understanding of interactions between large-scale cortical networks and the thalamus, which may interest a broader audience in neuroscience and clinical research.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
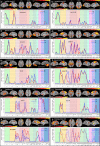


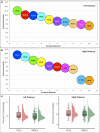
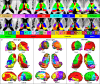

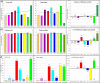


References
-
- Sherman, S. M. in Progress in Brain Research Vol. 149 107–126 (Elsevier, 2005). - PubMed
-
- Sherman, S. M. & Guillery, R. W. in Exploring the Thalamus and Its Role in Cortical Function 253–286 (MIT Press, 2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

