Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses identify novel genetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 36333501
- PMCID: PMC10165422
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01213-w
Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses identify novel genetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
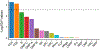
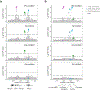
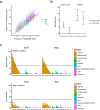
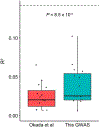
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a highly heritable complex disease with unknown etiology. Multi-ancestry genetic research of RA promises to improve power to detect genetic signals, fine-mapping resolution and performances of polygenic risk scores (PRS). Here, we present a large-scale genome-wide association study (GWAS) of RA, which includes 276,020 samples from five ancestral groups. We conducted a multi-ancestry meta-analysis and identified 124 loci (P < 5 × 10-8), of which 34 are novel. Candidate genes at the novel loci suggest essential roles of the immune system (for example, TNIP2 and TNFRSF11A) and joint tissues (for example, WISP1) in RA etiology. Multi-ancestry fine-mapping identified putatively causal variants with biological insights (for example, LEF1). Moreover, PRS based on multi-ancestry GWAS outperformed PRS based on single-ancestry GWAS and had comparable performance between populations of European and East Asian ancestries. Our study provides several insights into the etiology of RA and improves the genetic predictability of RA.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures




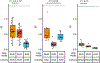



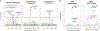


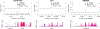

Comment in
-
Expanding genetic diversity and polygenic risk scores application in rheumatic disease studies: a call for inclusive research.Lancet Rheumatol. 2023 Oct;5(10):e572-e574. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00236-9. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 38251479 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ajeganova S & Huizinga TWJ Seronegative and seropositive RA: alike but different? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol 11, 8–9 (2015). - PubMed
-
- MacGregor AJ et al. Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 30–37 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Ishigaki K et al. Polygenic burdens on cell-specific pathways underlie the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet 49, 1120–1125 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR003096/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR069516/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA176726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 AR081023/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 21229/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049880/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR300826/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 19739/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- U01 HG012009/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 207491/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

